Vitamin D plays a crucial role in bone health, muscle movement, brain function, and immune defenses.
Unfortunately, vitamin D deficiency is common and can increase the risk of musculoskeletal problems, autoimmune diseases, mood disorders, and certain cancers.
Let’s look at common symptoms of vitamin D insufficiency and discover why most people benefit from taking vitamin D.

What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that regulates various physiological functions, including bone mineralization, muscle function, calcium balance, nerve transmissions, and immune defenses. Also known as the sunshine vitamin, the body produces vitamin D when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation in sunlight. UVB rays trigger a cascade of biochemical reactions that convert previtamin D3 into vitamin D3, which is converted into its active form in the liver and kidneys. The rate of vitamin D production depends on several factors, including average UVB light exposure, age, skin tone, body weight, health status, and geographical location. Because vitamin D is fat-soluble, it can be stored in fat cells and the liver for extended periods. However, lack of adequate sunlight exposure can deplete vitamin D levels and lead to deficiency. Watch the video below to learn how vitamin D affects every organ and tissue in the body.
Benefits of vitamin D
“Almost every cell in the human body has a vitamin D receptor,”explains Dr. Berg. “This indicates that vitamin D is crucial for the regulation of normal cellular function.” Research published by The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition supports the importance of a healthy vitamin D status for overall health. Here are four health benefits of vitamin D.
1. Skeletal health
Vitamin D stimulates the intestinal absorption of dietary calcium, and low vitamin D levels can quickly lead to calcium deficiency. Lack of sufficient calcium impairs bone tissue mineralization, linked to low bone density and an increased risk of fractures and osteoporosis in later life.
2. Strong immune defenses
Adequate vitamin D levels help regulate the production and activity of immune cells, including macrophages, T-cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, the body’s primary defense mechanisms against diseases and infections. Evidence published in Molecular Science suggests that “Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of developing immune-related diseases such as psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis.”
3. Improved mental health
Vitamin D supports neuronal health and regulates the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter needed for mood regulation. Vitamin D deficiency is linked to depression in teens and adults and may increase the risk of anxiety and other mood disorders.
4 . Lowers risk of cancer
Healthy vitamin D levels have been found to reduce prostate, colorectal, and breast cancer risk.
Although the exact role of vitamin D in cancer risk reduction is not fully understood, there is evidence that vitamin D can enhance the activity of immune cells that detect and eliminate carcinogenic cells.

Vitamin D3 vs. D2
Vitamin D naturally occurs as vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Although they have a similar chemical structure, vitamins D2 and D3 are very different.
Vitamin D3 is produced when skin is exposed to UVB radiation and can be found in a few foods, including egg yolks, fatty fish, fish liver oils, and organ meats.
In contrast, vitamin D2 is only found in certain types of yeasts and wild mushrooms exposed to UVB radiation.
Vitamin D2 is cheap to manufacture and often used in over-the-counter dietary supplements and fortified foods such as breakfast cereals, milk, and orange juice.
Vitamin D3 is more readily absorbed and significantly more effective in correcting and preventing deficiency than vitamin D2.
The importance of taking vitamin D with vitamin K2
While it’s well known that taking vitamin D supplementation promotes calcium absorption and healthy bones, the importance of vitamin K2 for skeletal and cardiovascular health is often overlooked.
While vitamin D3 enhances calcium absorption in the small intestines, vitamin K2 is needed to deposit circulating calcium into bone and teeth.
Combining vitamins D3 and K2 is crucial to ensure optimal bone tissue mineralization, which reduces the risk of low bone mass, soft bones, and increased risk of bone fractures.
In addition, taking vitamin D3 and K2 benefits cardiovascular health. Because vitamin K2 redirects calcium into bones, it plays a critical role in maintaining the health of your circulatory system.
Vitamin K deficiency, especially when taking a vitamin D or calcium supplement, can lead to elevated blood calcium levels. This greatly increases the risk of vascular calcification and the formation of arterial plaque, a leading cause of cardiovascular disease.

Identifying and managing vitamin D deficiency
A study published in Frontiers of Nutrition estimates that almost half of all U.S. adults have low vitamin D levels or are at risk of deficiency.
This leaves a significant proportion of the population at risk of skeletal issues, poor mental health, cardiovascular disease, and impaired immunity.
Let’s look at common causes and risk factors of vitamin D deficiency.
Causes and risk factors
Lack of adequate UVB exposure is a leading cause of low vitamin D status. People who live in regions with limited sunlight and those who spend most of their time indoors often don’t produce enough vitamin D to maintain healthy levels.
Vitamin D is stored in fat tissue, and excess body fat can trap vitamin D in fat cells. This reduces circulating levels of active vitamin D and explains why overweight or obese individuals can develop vitamin D deficiency despite adequate sunshine exposure.
Darker skin contains more melanin, a pigment that determines skin color, compared to lighter skin tones. Melanin reduces vitamin D production, which leaves people with darker skin tones at risk of vitamin D deficiency, especially if they live in regions with limited sunlight.
As you age, vitamin D metabolism typically slows down, significantly increasing the risk of low vitamin D stores in older adults.
Some medical conditions, such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can interfere with vitamin D absorption.
Research published in Nutrition Issues in Gastroenterology found a high prevalence of severe vitamin D deficiency among patients with gastrointestinal health issues.
 Symptoms and diagnosis
The symptoms of low vitamin D can be subtle and nonspecific, making it challenging to identify and diagnose vitamin D deficiency based on clinical manifestations alone.
Fortunately, vitamin D status can easily be evaluated with a simple blood test that measures the concentration of active vitamin D in your blood.
Serum vitamin D levels below 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L) indicate deficiency, levels between 20 and 30 ng/mL (50-75 nmol/L) are insufficient, and levels above 50 nmol/L (20 ng/mL) are generally adequate for most healthy adults.
Here are common signs of vitamin D deficiency:
Symptoms and diagnosis
The symptoms of low vitamin D can be subtle and nonspecific, making it challenging to identify and diagnose vitamin D deficiency based on clinical manifestations alone.
Fortunately, vitamin D status can easily be evaluated with a simple blood test that measures the concentration of active vitamin D in your blood.
Serum vitamin D levels below 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L) indicate deficiency, levels between 20 and 30 ng/mL (50-75 nmol/L) are insufficient, and levels above 50 nmol/L (20 ng/mL) are generally adequate for most healthy adults.
Here are common signs of vitamin D deficiency:
- Bone pain
- Muscle weakness
- Hair loss
- Depression
- Frequent infections
- Acne
- Poor wound healing
- Brittle bones
- Brain fog and memory problems
If you are concerned about your vitamin D levels or experience vitamin D deficiency-related symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider to evaluate your vitamin D blood levels and assess your overall health status.
Treatment and prevention
Vitamin D deficiency is most commonly treated with vitamin D3, which is the preferred supplemental form as it’s more effective at raising vitamin D blood levels compared to vitamin D2.
Depending on the severity of the deficiency and vitamin D dosage, levels typically improve within six to eight weeks of regular vitamin D3 intake.
If deficiency is related to medication use or underlying medical issues such as malabsorption or liver or kidney problems, it’s essential to address and manage these underlying causes as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
While sun exposure is a natural way to prevent vitamin D deficiency, it may not be enough to maintain optimal vitamin D stores, and supplementing with vitamin D is an effective way to promote healthy levels.

Vitamin D dosage
The correct vitamin D dosages depend on factors such as your vitamin D blood levels, sunlight exposure, skin tone, health status, and body weight.
A dose of 600 IU daily is typically suggested by most healthcare providers. However, 600 IU of vitamin D may not be enough to achieve healthy vitamin D stores.
If you have vitamin D deficiency, lack adequate sunlight exposure, are overweight or obese, have a darker skin tone, or suffer a gastrointestinal condition, you may require around 10,000 IU of vitamin D3 daily to promote a healthy body.
In addition, a study published in Women’s Health suggests that pregnant and lactating women require more vitamin D to support their baby’s development and should consult with a healthcare provider to determine a safe and adequate vitamin D dosage.
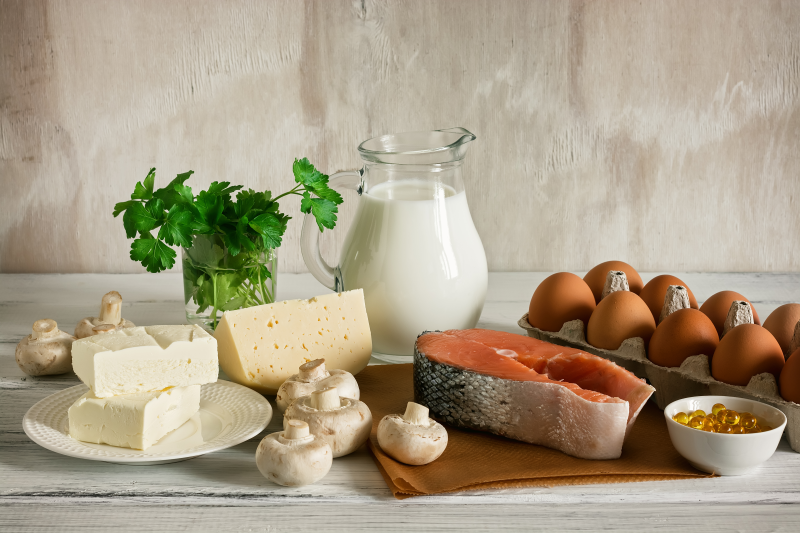

Sources of vitamin D
The body produces vitamin D in response to sunlight and can absorb it via the intestines from foods and supplements. While sunlight exposure is the body’s primary source of vitamin D, some dietary sources include fatty fish, cod liver oil, egg yolks, and fortified foods such as milk and orange juice.
Can you get enough vitamin D from food alone?
A report published by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services suggests that relying on food sources to obtain the recommended dietary allowance of vitamin D isn’t adequate and significantly increases the risk of deficiency. Not only is there a limited number of vitamin D-rich foods, but it’s also believed that only 50 percent of dietary vitamin D is absorbed into the bloodstream.
Vitamin D and sunlight: how much sun exposure do you need?
General guidelines suggest between 10 and 30 minutes of midday sun exposure several times a week without sunscreen can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels.
However, locations at latitudes greater than 42° north of the equator have lower UVB radiation, and significantly longer periods in sunlight may be needed to stimulate adequate vitamin D production.
In addition, older individuals and those with darker skin tones typically have a reduced rate of vitamin D production, which can make it challenging to get enough vitamin D from sunlight exposure alone.

How to choose a quality vitamin D supplement
While vitamin D supplements are widely available, the quality and effectiveness of vitamin D-containing supplements can differ significantly. Vitamin D3 is a more potent form compared to vitamin D2 and is more effective in correcting vitamin D deficiency and maintaining optimal levels. Low-dose vitamin D products often fail to maintain a healthy vitamin D status, and it’s recommended to opt for a supplement that contains at least 5000 IU of vitamin D3 per serving. It’s equally important to choose a vitamin D supplement with added vitamin K2. The best ratio of vitamin D3 to K2 is 1000:10, which means it contains 10 mcg of vitamin K2 per 1000 IU of vitamin D3. To maximize the health benefits of vitamin D3, it’s crucial to enhance its intestinal absorption. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that requires fatty acid and bile salts to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Look for high-quality vitamin D supplements containing ox bile and medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), especially if you are deficient, overweight, or have gastrointestinal conditions. When vitamin D3 is taken in combination with MCTs and bile acids, it increases its solubility and improves fat emulsification in the digestive system, which can significantly enhance the absorption of vitamin D.
Vitamin D risks
Vitamin D supplementation is generally considered a safe and effective strategy to prevent or correct a deficiency. However, compared to water-soluble vitamins that are readily excreted, fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin D can accumulate in the body and lead to adverse health effects. Here are some risks associated with vitamin D supplementation.
Vitamin D toxicity
Vitamin D toxicity, also known as hypervitaminosis D, is characterized by an excessive buildup of vitamin D in the body. Hypervitaminosis D can develop when too much vitamin D is taken for prolonged periods or may be linked to certain medical conditions that disrupt the body’s ability to regulate vitamin D levels. Common signs of vitamin D toxicity include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Confusion
- Kidney stones
- Elevated blood calcium levels
Vitamin D interactions
While some common drugs can deplete vitamin D, there is evidence that vitamin D can increase the risk of side effects of certain medications, including diuretics and anti-seizure drugs. Vitamin D may also alter the metabolism of drugs used to treat cancer and can increase the risk of excessive blood calcium levels when combined with calcium supplementation. It’s crucial to discuss potential drug interactions with a healthcare provider before starting vitamin D supplementation if you are taking prescription or over-the-counter medications to minimize the risk of side effects.
Potential side effects
People with a sensitive digestive tract can experience gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and stomach pains after taking vitamin D.
Liquid vitamin D3 drops or vitamin D supplements that contain MCTs and ox bile are gentle on the stomach and can reduce the risk of intestinal issues.
It’s important to note that individuals with hyperparathyroidism and certain cancers, such as lymphoma or bone cancer, should not take extra vitamin D.
These conditions can cause elevated calcium levels, which could be exacerbated by vitamin D and lead to an increased risk of soft tissue calcification linked to arterial stiffness and heart disease. 
Key takeaways
Vitamin D is critical for bone health, immune defenses, and cognitive function and may lower the risk of autoimmune diseases, depression, and certain cancers. Vitamin D deficiency is widespread, and supplementation is a safe and effective strategy to maintain healthy vitamin D levels. To maximize the health benefits of vitamin D, it’s recommended to choose vitamin D3 in combination with vitamin K2 and opt for a product that contains MCTs and ox bile to enhance its intestinal absorption.
FAQ
1. What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that’s involved in various physiological functions. The body produces vitamin D in response to sunlight exposure. When ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation penetrates the skin, a complex cascade of biochemical reactions is triggered that convert pre-vitamin D into its active form.
2. What does vitamin D do for the body?
Almost all cells in the body have a vitamin D receptor, which indicates the importance of this nutrient for normal cellular functioning. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating calcium balance, bone mineralization, brain function, and immune defenses.
3. What are the benefits of vitamin D?
An extensive systematic review and meta-analysis of existing studies revealed that adequate vitamin D levels are strongly linked to a reduced risk of osteoporosis, certain cancers, autoimmune diseases, mood disorders, and age-related cognitive decline.
4. How can I get vitamin D naturally?
The body can produce vitamin D naturally when the skin is exposed to sunshine, and 10 to 30 minutes of midday sun several times a week can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels. However, sunlight exposure alone may not be enough for individuals who live at latitudes higher than 42° north of the equator and those who are overweight, elderly, or have a darker skin tone.
5. Are vitamin D supplements safe?
Vitamin D supplements are generally considered safe for most people when taken as directed by a healthcare professional.
6. How much vitamin D do I need daily?
Your ideal vitamin D3 dosage depends on your vitamin D blood levels, average sunlight exposure, skin tone, and health status. While general recommendations suggest around 600 IU of vitamin D daily, you may need a significantly higher dose of up to 10,000 IU daily to correct a vitamin D deficiency.
7. Should I take vitamin D2 or vitamin D3?
Vitamin D3 is a more potent form of vitamin D that’s readily absorbed into the bloodstream and has been found to be significantly more effective at raising vitamin D levels compared to vitamin D2.
8. What are the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency?
Common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include frequent infections, hair loss, bone pain, weak muscles, acne, depression, and memory problems.
9. What causes vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency is primarily caused by a lack of adequate sunlight exposure. Other factors contributing to low vitamin D status include medical conditions that reduce intestinal vitamin D absorption and certain medications that can impair vitamin D metabolism, such as antifungal medications, laxatives, and common weight-loss drugs. In addition, older individuals and those with a darker skin tone often don’t produce adequate amounts of vitamin D, leaving them at risk of deficiency.
10. Can you get vitamin D from food?
While there are a few dietary sources of vitamin D, including egg yolks, fatty fish, and organ meats, these foods contain only small amounts and won’t support healthy vitamin D levels.
11. What are the symptoms of vitamin D toxicity?
Symptoms of vitamin D toxicity include nausea, vomiting, confusion, muscle pain, poor kidney function, unexplained weight loss, and elevated blood calcium levels.
12. Does vitamin D interact with medications?
Yes, vitamin D can interact with medications and increase the risk of side effects of certain diuretics and lithium-containing anti-seizure drugs.
13. Can bile salts enhance vitamin D absorption?
Yes, bile salts play a crucial role in enhancing the absorption of vitamin D. Bile salts are produced by the liver and released into the digestive tract, where they help solubilize fats and fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D, making it easier for the body to absorb vitamin D into the bloodstream.
14. Why do I need to take vitamin K2 with vitamin D?
Vitamin D stimulates calcium absorption, and vitamin K helps deposit calcium into bone tissue. Taking vitamin D without vitamin K can lead to calcium accumulation in the blood, a major risk factor for soft tissue calcification and arterial plaque formation.
15. Can MCT oil increase vitamin D bioavailability?
Yes, medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil can enhance the bioavailability of vitamin D. Vitamin D is fat-soluble, and MCT oil offers a quickly absorbed and metabolized source of fat that helps solubilize vitamin D, which makes it more available for absorption.







