Keto and Fatty Liver: How to Reduce Liver Fat Fast

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated
Fat accumulation in the liver can result in serious metabolic imbalances and liver damage—unfortunately, it's estimated that almost 25 percent of adults have some degree of fatty liver disease.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) typically develops due to a high-carb diet and is more common in individuals with type 2 diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance.
Learn how a low-carb, high-fat keto diet supports your liver health and reduces liver fat quickly!
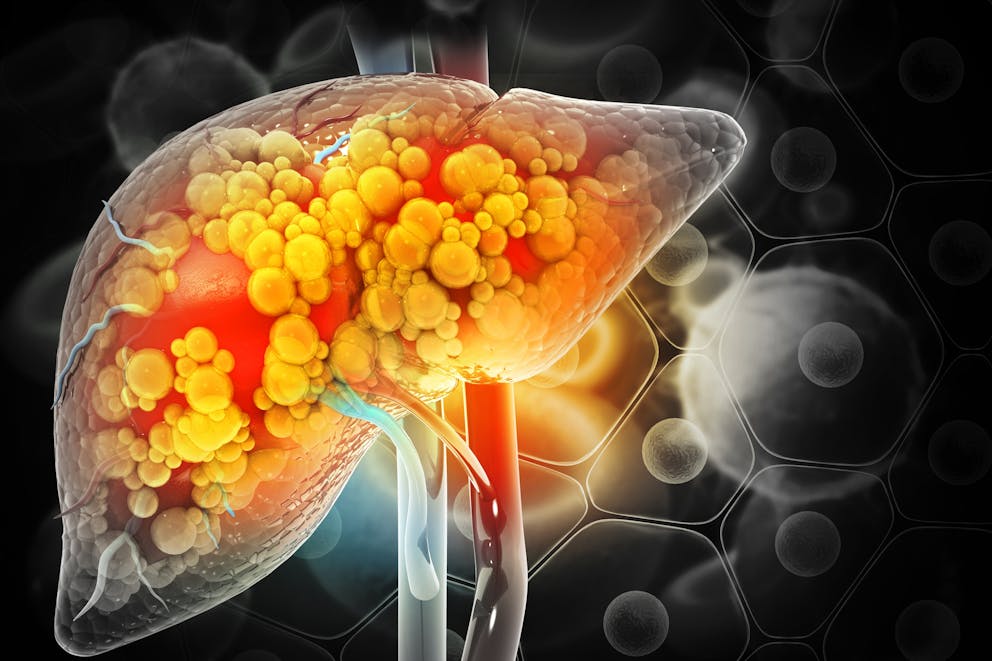
How to reduce liver fat with keto
Restricting carbohydrates prevents fatty liver and helps to reduce existing liver fat, making keto an ideal diet to support your liver health.
During ketosis, the liver converts dietary fats and stored fatty acids into ketones to fuel your body. Ketosis also stimulates the increased production of enzymes that promote fatty acid oxidation and speed up the breakdown of fats stored in the liver.
In addition, keto helps to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and keeps your cells sensitive to insulin, preventing the storage of fats in liver cells and significantly reducing the risk of fatty liver disease.
Several studies confirm that a ketogenic diet helps to reduce liver fat in individuals with NAFLD and significantly improves liver function.
One study published in Cell Metabolism found that a low carbohydrate keto diet reduced liver fat by over 40 percent in overweight and obese individuals. The authors observed that carbohydrate restriction leads to “a dramatic reduction of liver fat.”
Here are three steps you can take to maximize the reduction of liver fat on keto.
1. Follow Healthy Keto®
While a low-carb diet is crucial to reduce liver fat, following a nutritious diet is equally important, making Healthy Keto® a perfect choice to support your liver health.
Healthy Keto is a low-carb, high-fat diet incorporating nutrient-rich, high-quality foods, including non-GMO organic vegetables, grass-fed beef, full-fat organic dairy and eggs, and wild-caught fish. This supports your nutritional needs for optimal health while burning liver fat.
2. Combine keto with intermittent fasting
Doing keto and intermittent fasting is an excellent combination that helps your body to stay in ketosis and maximizes fat burning.
Intermittent fasting is a mealtime schedule that cycles between fasting and eating periods.
“During fasting, your metabolism relies on stored fatty acids as an energy source,” says Dr. Berg. “This means your liver utilizes the readily available excess fat stored in liver cells first to generate ketones to fuel your cells.”
3. Eat choline-rich foods
Choline is an essential nutrient for liver health and is closely connected to fat metabolism. Research published in Nutrients suggests that low choline intake increases the risk of liver fat accumulation and fatty liver disease.
Choline is converted to phosphatidylcholine, an essential cellular compound needed to oxidize fatty acids and convert them into energy. Without adequate choline, fat remains in cells and can’t be used for energy production.
Here are some keto-approved foods rich in choline:
Beef
Beef liver
Eggs
Chicken
Fish
Full-fat dairy products
Sunflower seeds
Watch the video below to learn how a high-fat keto diet helps to reverse a fatty liver.
What is keto?
The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat, moderate-protein diet that shifts your metabolism to burn fat instead of carbs and sugars for energy.
As the liver breaks down fat, it produces large quantities of ketones, a metabolic by-product of fatty acid oxidation and a very efficient fuel source. In fact, your heart, brain, and muscles prefer ketones for energy compared to relying on sugars and carbohydrates.
Ketones enter your circulation to fuel your body—this state is known as ketosis. To stay in ketosis, consume no more than 20 to 50 grams of carbs daily.
Many lifestyle diseases like obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome develop from chronically elevated blood glucose and insulin levels.
A high-fat diet combined with carbohydrate restriction keeps blood sugar levels balanced and supports healthy insulin levels, which improves insulin sensitivity, lowers inflammation, and supports healthy body weight.

What is fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease, also known as the silent killer due to the lack of early warning signs and symptoms, is caused by excessive amounts of liver fat.
Fatty liver disease can be grouped into two types:
1. Alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused by prolonged alcohol use resulting in liver cell damage, inflammation, fat accumulations, and loss of liver function.
2. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the accumulation of liver fat caused by dietary and lifestyle factors. It’s strongly associated with metabolic disorders such as obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Other risk factors for developing NAFLD include a high-carb diet, a sedentary lifestyle, excessive fructose consumption, and genetic predisposition.
Fatty liver disease is typically diagnosed by assessing serum liver enzymes, liver scans, or a liver biopsy.
If left untreated, fatty liver can progress to severe liver diseases, such as hepatic steatosis, which is linked to liver inflammation and increases the risk of developing cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
If you suspect that you may have developed liver fat, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine your liver health and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
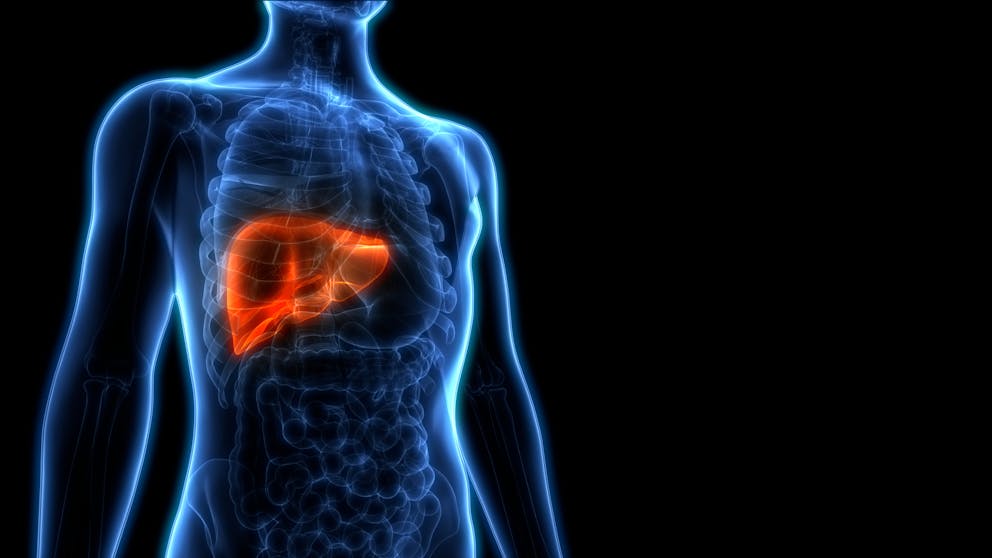
Does dietary fat cause liver fat?
It may seem counterintuitive, but dietary fat is rarely linked to the development of fatty liver.
Fat accumulations in the liver are typically caused by excessive calorie intake, snacking, and a diet high in refined carbs and sugars.
Eating sugars and carbs causes the release of insulin, a metabolic hormone that helps to keep blood sugar in healthy ranges.
Over long periods, high amounts of carbs and sugar cause your cells to become less reactive to insulin, leading to insulin resistance, a primary risk factor for developing fatty liver disease.
A high carb intake in combination with insulin resistance results in elevated blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia. Because hyperglycemia is toxic to the body, the liver converts excess blood sugar into fatty acids, which are stored in liver cells and responsible for developing fatty liver disease.
Watch the video below to learn how to reduce liver fat by almost 50 percent in two weeks using a low-carb diet.
Key takeaways
A low-carb, high-fat keto diet is crucial to reduce liver fat and significantly lowers the risk of fatty liver disease.
Restricting sugar and carb intake shifts your metabolism to utilize stored fatty acids in the liver to generate ketones, a potent energy source that fuels your cells during ketosis.
Combining Healthy Keto with intermittent fasting supports healthy blood sugar levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and maximizes keto's fat-burning effects, which helps dissolve liver fat fast!
FAQ
1. Is a ketogenic diet good for fatty liver disease?
Research suggests that a low-carbohydrate diet like keto significantly reduces liver fat in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Because keto shifts your metabolism to burn fats instead of sugars, the liver utilizes fatty deposits in liver cells to generate energy.
2. How long does it take to reverse fatty liver with keto?
That depends on many factors, including your body weight, sensitivity to insulin, and the severity of fatty liver disease.
However, one study found that a ketogenic diet reduced liver fat by more than 40 percent in two weeks in obese individuals with fatty liver disease.
3. What happens to the liver during ketosis?
During ketosis, your liver breaks down stored fatty acids and dietary fats to produce ketones, a very efficient fuel source for your cells.
Ketosis also triggers the production of liver enzymes needed to utilize fatty acids as a fuel source, which stimulate fat burning and help eliminate fat accumulations in liver cells.
4. Is a low-carb diet best for fatty liver treatment?
A low-carb diet is one of the most important steps you can take to support liver health and reduce liver fat. A low-carb keto diet promotes healthy insulin levels and lowers the risk of insulin resistance, a significant risk factor for fatty liver.
5. Can ketosis cause fatty liver?
Ketosis doesn’t cause fatty liver. In fact, ketosis can significantly reduce liver fat by stimulating the use of stored liver fat to generate ketones, an energy source that fuels the cells in your body during ketosis.
6. Can keto make fatty liver worse?
Keto won’t worsen nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which results from a high-carb diet leading to insulin resistance, a significant risk factor for fatty liver disease.
Keto improves insulin sensitivity and supports balanced blood sugar control, which prevents fat accumulation in the liver. Ketosis stimulates the breakdown of stored fatty acids in the liver, which reduces liver fat and improves liver function.
7. How does keto affect fatty liver?
Keto has been found to reduce liver fat and significantly improve liver health. A low-carb diet shifts your metabolism to burn fats instead of sugars, which stimulates the liver to utilize stored fatty acids to generate energy, directly reducing liver fat.
8. Why does a fatty keto diet decrease fatty liver?
Because keto is a low-carb diet, the liver burns fats to produce energy instead of sugars. This prevents fat accumulation in the liver and, at the same time, triggers the utilization of stored fatty acids in liver cells to generate energy which reduces fatty liver.
Previous blog
Damage Control From Your Cheat Day on KetoNext blog
The Most Important Blood TestTags

Popular
08/21/2024
55K views
02/23/2025
46.3K views
11/18/2024
277.5K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




