Hypoglycemia Without Symptoms
If you're struggling with hypoglycemia, you know how frustrating and scary those sudden drops in blood sugar can be. The shakiness, the cold sweats, the brain fog... it's no fun.
But what if I told you there's a way to take control of your blood sugar and say goodbye to those hypoglycemic episodes for good?
Enter the ketogenic diet. By shifting your body's primary fuel source from glucose to ketones, you can stabilize your blood sugar levels and kiss those hypoglycemic crashes goodbye. And the best part?
It's not just about managing symptoms - a ketogenic diet can actually improve your overall metabolic health and help you feel your best.
So, if you're ready to take charge of your hypoglycemia and experience the life-changing benefits of a ketogenic lifestyle, keep reading. I promise, it's not as complicated as it sounds!
Understanding Hypoglycemia and Its Types
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can be a challenging condition to manage, especially if you have diabetes. But even if you don't have diabetes, you can still experience hypoglycemia.
In this post, we'll explore the different types of hypoglycemia, their symptoms, and how they manifest in both diabetics and non-diabetics.
It's important to note that hypoglycemia is characterized by low blood sugar levels. In diabetics, hypoglycemia is defined as blood sugars less than 70 mg/dL, while in non-diabetics, it's defined as blood sugars less than 54 mg/dL.
Hypoglycemia Without Symptoms
Did you know that hypoglycemia can occur without noticeable symptoms during ketogenic diets or fasting?
This is because when you're in a state of ketosis or fasting, your body is using ketones for fuel instead of glucose, so your blood sugar levels may be lower than usual without causing any symptoms.
Pseudo-Hypoglycemia
Pseudo-hypoglycemia, also known as idiopathic postprandial syndrome, is a condition where you experience hypoglycemic symptoms without actual low blood sugar levels.
This can be caused by a rapid drop in blood sugar after eating, even if your blood sugar levels are still within the normal range.
Reactive Hypoglycemia
Reactive hypoglycemia occurs after eating and is different from spontaneous hypoglycemia that occurs during fasting. This type of hypoglycemia is often caused by an overproduction of insulin in response to a meal, leading to a rapid drop in blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia can include trouble talking, confusion, irritability, hunger, carb cravings, sweating, shaking, weakness, fainting, vision problems, and headaches.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to check your blood sugar levels and treat the hypoglycemia accordingly.
Causes and Triggers of Hypoglycemia
Now that we've covered the different types of hypoglycemia, let's explore the various causes and triggers of hypoglycemia in both diabetics and non-diabetics.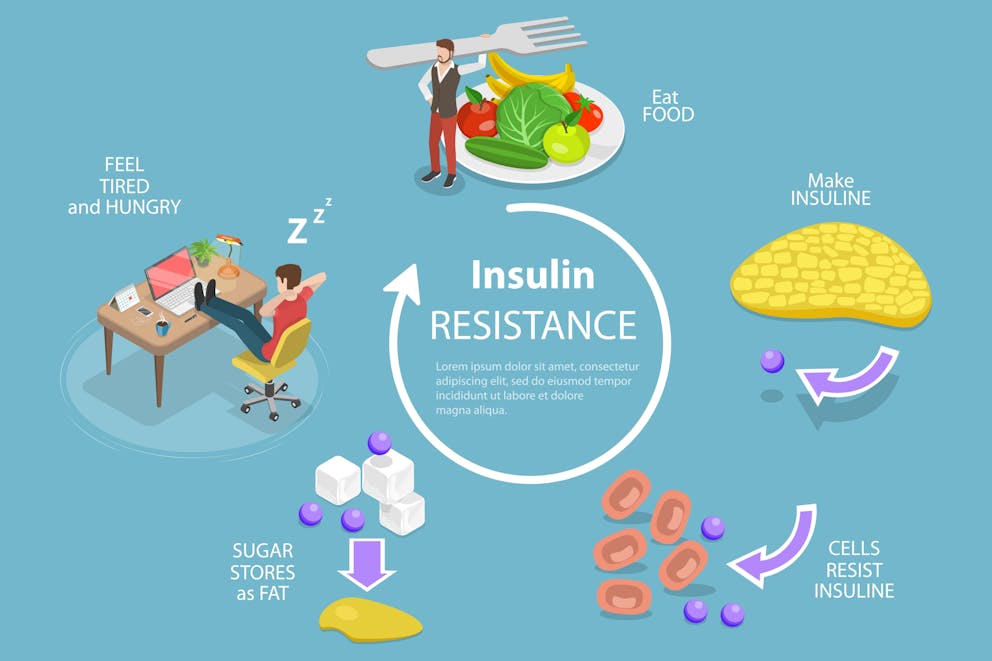
Insulin Resistance
High carbohydrate intake can lead to insulin resistance, which may cause pseudo-hypoglycemia. When you consume a lot of carbs, your body has to produce more insulin to keep your blood sugar levels in check.
Over time, this can lead to insulin resistance, where your body becomes less sensitive to insulin and requires more of it to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Insulin resistance caused by constant stimulation of insulin due to high carb consumption can lead to pseudo-hypoglycemia.
This is because your body may be producing too much insulin in response to the carbs you're eating, leading to a rapid drop in blood sugar levels even if they're still within the normal range.
Medication-Induced Hypoglycemia
For diabetics, hypoglycemia can be caused by taking too much insulin or other medications that increase insulin levels. This is why it's so important for diabetics to work closely with their healthcare provider to adjust their medication doses as needed.
Reactive hypoglycemia occurs after eating and is different from spontaneous hypoglycemia that occurs during fasting. This type of hypoglycemia is often caused by an overproduction of insulin in response to a meal, leading to a rapid drop in blood sugar levels.
Managing Hypoglycemia with a Ketogenic Diet
If you're struggling with hypoglycemia, adopting a ketogenic diet can be a game-changer. In this section, we'll discuss how a ketogenic diet can help manage and stabilize blood sugar levels effectively.
Benefits of a Low-Carb Diet
A low-carb diet, like the ketogenic diet, can help reduce insulin levels and stabilize blood sugar. When you consume fewer carbs, your body produces less insulin, which can help prevent the rapid drops in blood sugar that can lead to hypoglycemia.
The main solution for hypoglycemia is adopting a ketogenic diet to reduce insulin levels and stabilize blood sugar. By following a ketogenic diet, you'll be consuming more healthy fats and protein, which can help keep your blood sugar levels stable throughout the day.
Protein Intake
Increasing your protein consumption can also aid in managing hypoglycemic episodes. Protein takes longer to digest than carbs, which means it can help slow down the absorption of glucose into your bloodstream and prevent rapid drops in blood sugar.
Consuming more protein and following a low-carb diet can help manage hypoglycemia. Aim to include a source of protein at every meal and snack, such as eggs, meat, fish, or tofu.
Practical Tips for Implementing a Ketogenic Diet
Now that we've covered the benefits of a ketogenic diet for managing hypoglycemia, let's dive into some practical tips for implementing this way of eating.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
One of the most important things you can do when managing hypoglycemia with a ketogenic diet is to monitor your blood glucose levels regularly. Use a glucose monitor to keep track of your blood sugar levels throughout the day, especially before and after meals.
By monitoring your blood glucose levels, you'll be able to identify patterns and triggers that may be causing your hypoglycemia. This information can help you make adjustments to your diet and lifestyle as needed to better manage your blood sugar levels.
Choosing Healthy Fats
When following a ketogenic diet, it's important to choose healthy fats to incorporate into your meals and snacks. Some great options include olive oil, coconut oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds.
Staying Hydrated
Staying hydrated is crucial when following a ketogenic diet, especially if you're managing hypoglycemia. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day to support your body's metabolic processes and help flush out toxins.
Dehydration can actually worsen hypoglycemia symptoms, so it's important to make sure you're getting enough fluids throughout the day. You can also incorporate other hydrating beverages like herbal tea, bone broth, and low-carb electrolyte drinks.
Additional Strategies for Blood Sugar Regulation
In addition to following a ketogenic diet, there are other strategies you can use to help regulate your blood sugar levels and manage hypoglycemia. Let's explore a couple of these strategies in more detail.

Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is a powerful tool that can be used in conjunction with a ketogenic diet to further stabilize blood sugar levels.
By limiting your eating window to a shorter period of time each day, you can help reduce insulin resistance and improve your body's ability to regulate blood sugar.
There are many different intermittent fasting protocols to choose from, such as the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window) or the 5:2 method (eating normally for 5 days and restricting calories to 500-600 per day on the other 2 days).
Find a protocol that works best for your lifestyle and preferences.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is another important strategy for managing hypoglycemia and regulating blood sugar levels.
Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, which means your body becomes more efficient at using insulin to transport glucose into your cells for energy.
Aim to incorporate at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. If you're new to exercise, start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts over time.
Physical activity plays a crucial role in improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, so make it a priority in your overall hypoglycemia management plan.
Managing hypoglycemia with a ketogenic diet, intermittent fasting, and regular exercise can be a powerful combination for stabilizing blood sugar levels and improving overall health.
As always, be sure to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that takes into account your unique needs and medical history.
Sweet Stability
Managing blood sugar levels and hypoglycemia on a keto diet can be effectively achieved with the right sweeteners. Allulose and erythritol are two popular choices that offer a sweet taste without the spikes in blood sugar.
Allulose, a rare sugar found naturally in small amounts in certain fruits, is absorbed by the body but not metabolized, providing sweetness with minimal caloric impact.
Erythritol, a sugar alcohol, also offers a sweet flavor without raising blood sugar levels, making it an excellent choice for keto enthusiasts.
When comparing allulose vs erythritol, both serve as excellent tools for stabilizing blood sugar and managing hypoglycemia while maintaining the low-carb principles of a keto diet.
Managing Unexpected Side Effects During Fasting
One lesser-known side effect of fasting or a ketogenic diet is feeling cold while fasting. This occurs as your body shifts from burning glucose to fat, a process that can temporarily reduce heat production.
Additionally, the reduced calorie intake and potential for lower blood sugar levels during fasting may contribute to this sensation.
While it’s typically harmless, it can be uncomfortable for some. To minimize this effect, ensure you’re staying hydrated, replenishing electrolytes, and dressing warmly during fasting periods.
Conclusion
Managing hypoglycemia with a ketogenic diet is a game-changer. By reducing your carb intake, increasing healthy fats, and prioritizing protein, you can stabilize your blood sugar levels and say goodbye to those scary hypoglycemic episodes.
But it's not just about symptom management - a ketogenic diet can improve your overall metabolic health, boost your energy levels, and even support healthy weight loss.
With a little planning and some simple lifestyle tweaks, you can experience the life-changing benefits of a ketogenic approach to hypoglycemia management.
So, what are you waiting for? Give the ketogenic diet a try and take control of your hypoglycemia today. Your body (and your taste buds) will thank you!
Previous blog
Foods That Mimic Body Parts
Popular
08/21/2024
55.7K views
02/23/2025
46.8K views
11/18/2024
281.1K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




