Hormonal Hair Loss
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, especially when it's triggered by hormonal changes. Many people don't realize that hormones play a crucial role in the health and growth of our hair.
Understanding the causes of hormonal hair loss is the first step toward finding effective solutions. As someone who's spent years researching and helping people with hair health, I've seen firsthand how hormonal imbalances can wreak havoc on our locks.
Let's explore the science behind why our hair sometimes decides to jump ship.
The Hormone-Hair Connection: Understanding the Basics
Before we get into hormonal hair loss causes, it's important to understand how hormones influence our hair growth cycle. Our hair goes through three main phases: growth (anagen), transition (catagen), and resting (telogen).
Hormones can affect each of these stages, either prolonging or shortening them. When hormones are out of whack, it can lead to premature shifting of hair follicles into the resting phase. This results in increased shedding and thinning.
Key Hormones Affecting Hair Growth
Several hormones play a role in hair health:
Androgens (like testosterone and DHT)
Estrogen
Thyroid hormones
Cortisol
Insulin
Each of these can impact hair growth in different ways. Let's explore how imbalances in these hormones can lead to hair loss.
Cortisol: The Stress Hormone's Impact on Hair
Cortisol, often called the "stress hormone," can be a major player in hormonal hair loss causes. When our bodies are under stress, cortisol levels spike. This can have two different effects on our hair.
Low Cortisol and Autoimmune Hair Loss
In some cases, prolonged stress can lead to adrenal fatigue and low cortisol levels. This can weaken our immune system, potentially triggering autoimmune responses that attack hair follicles. This type of hair loss often presents as patchy baldness, known as alopecia areata.
High Cortisol and Protein Breakdown
On the flip side, chronically high cortisol levels can lead to protein breakdown in the body. Since our hair is made primarily of protein (keratin), this can result in weakened hair strands and increased shedding.
To combat stress-related hair loss, it's crucial to find effective stress management techniques. This might include meditation, regular exercise, or speaking with a therapist.
Estrogen: The Female Hormone's Role in Hair Health
Estrogen is typically thought of as a female hormone, but it plays a vital role in hair growth for both men and women. Fluctuations in estrogen levels can be one of the key hormonal hair loss causes. Family history can also play a part.
Estrogen Dominance and Thyroid Function
When estrogen levels are too high compared to other hormones (a condition known as estrogen dominance), it can inhibit thyroid function. The thyroid gland is crucial for regulating our metabolism, including the rate of hair growth and renewal.
Estrogen dominance can occur during pregnancy, certain phases of the menstrual cycle, or when taking birth control pills. It can also happen due to exposure to environmental estrogens or certain health conditions.
Postpartum Hair Loss
Many new mothers experience hair loss after giving birth. This is due to the dramatic drop in estrogen levels following pregnancy.
The sudden decrease in estrogen can cause a large number of hair follicles to enter the resting phase simultaneously, leading to noticeable hair loss a few months postpartum.
Fortunately, postpartum hair loss is usually temporary. Hair typically regrows within 6-12 months as hormone levels stabilize.
Testosterone and DHT: The Male Hormone Connection
While testosterone is often considered a male hormone, it's present in both men and women and can be a significant factor in hormonal hair loss causes. Chemical treatments and radiation treatment are also known factors.
The DHT Factor
Testosterone can be converted into a more potent form called dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase.
DHT is known to bind to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing hair. This process is what causes vellus hair to form.
This process is the primary cause of male pattern baldness, but it can affect women too, especially during menopause when estrogen levels drop, allowing testosterone to have a more pronounced effect.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) and Androgen Excess
PCOS is a common hormonal disorder that can lead to hair loss in women. It's characterized by an excess of androgens (male hormones), which can cause thinning hair on the scalp while promoting unwanted hair growth on the face and body.
Women with PCOS often struggle with insulin resistance, which brings us to our next hormonal hair loss cause.
Insulin: The Blood Sugar Balancing Act
Insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, can indirectly contribute to hair loss when it's out of balance. Blood pressure is important for your overall health, but it is not directly related to hair loss.
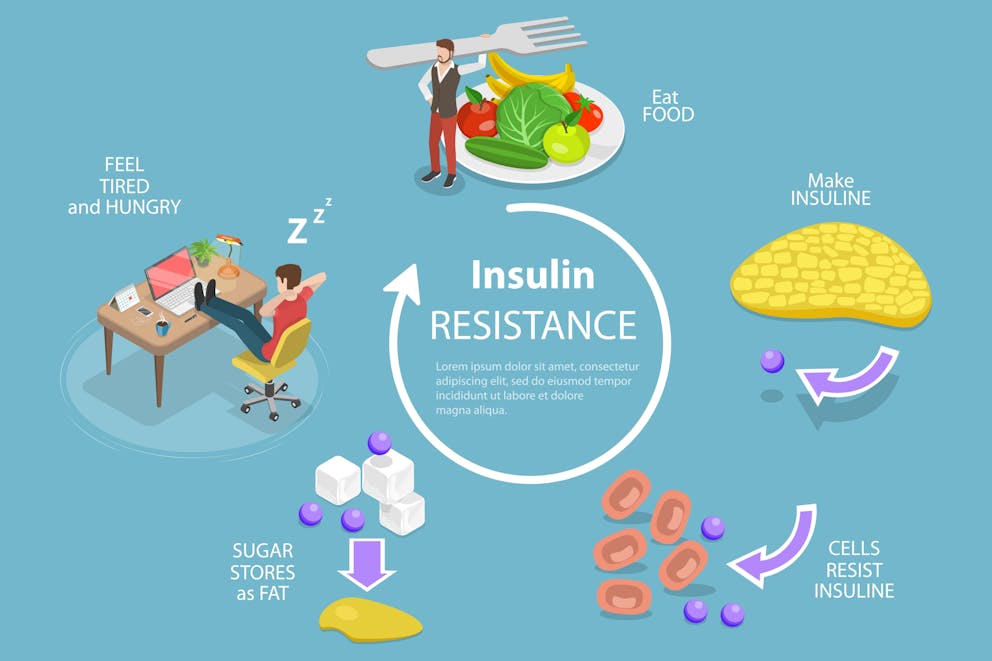
Insulin Resistance and Androgen Production
When our bodies become resistant to insulin (often due to a diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugars), it can lead to increased androgen production. As we've learned, excess androgens can contribute to hair loss.
The Diabetes Connection
People with diabetes or pre-diabetes are at higher risk for hair loss due to the effects of insulin resistance on hormone balance. Managing blood sugar levels through diet and lifestyle changes can help mitigate this risk.
Thyroid Hormones: The Metabolism Masters
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate our metabolism, including the rate at which our hair grows and sheds. Both an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) and an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can lead to hair loss.
Hypothyroidism and Hair Loss
Hypothyroidism is more commonly associated with hair loss. When thyroid hormone levels are low, it can slow down hair growth and lead to thinning hair. People with hypothyroidism may also notice loss of the outer third of their eyebrows.
The Liver-Thyroid Connection
Interestingly, thyroid issues often stem from liver or gallbladder problems. The liver plays a crucial role in converting thyroid hormones into their active form. If liver function is impaired, it can indirectly lead to hair loss through its effect on thyroid hormone activation.
Menopausal Hair Loss: A Hormonal Perfect Storm
Menopause represents a significant shift in a woman's hormonal landscape, and it's one of the most common hormonal hair loss causes in older women. Vitamin deficiencies can also contribute to hair loss in women of all ages.
The Estrogen-Testosterone Balance
During menopause, estrogen levels decrease dramatically. However, testosterone levels don't drop as much. This relative increase in testosterone (and its conversion to DHT) can lead to hair thinning similar to male pattern baldness.
Managing Menopausal Hair Loss
While we can't stop menopause, we can take steps to support our hair health during this transition. This might include:
Eating a nutrient-rich diet high in protein and healthy fats
Managing stress levels
Using gentle hair care practices
Considering supplements that support hair growth
Addressing Hormonal Hair Loss: A Holistic Approach
When it comes to hormonal hair loss causes, it's crucial to take a holistic approach. Simply treating the symptoms without addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances is unlikely to provide long-term results.
Dietary Interventions
Our diet plays a significant role in hormone balance. Focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods can help support healthy hormone levels. Some key dietary strategies include:
Reducing sugar and refined carbohydrate intake to support insulin sensitivity
Eating plenty of healthy fats to support hormone production
Consuming adequate protein for hair growth
Including foods rich in vitamins and minerals that support hair health, such as zinc, iron, and vitamins A, C, and E
Lifestyle Modifications
Beyond diet, several lifestyle factors can influence our hormone balance and hair health:
Regular exercise to support insulin sensitivity and reduce stress
Adequate sleep to allow for proper hormone regulation
Stress management techniques
Avoiding environmental toxins that can disrupt hormone balance
Supplementation and Natural Remedies
In some cases, targeted supplementation can help address hormonal imbalances and support hair growth. Some options to consider include:
Saw palmetto for reducing DHT levels
Adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha for stress management
Biotin and other B vitamins for hair growth
Omega-3 fatty acids for reducing inflammation
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you're dealing with hormonal imbalances.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many cases of hormonal hair loss can be addressed through lifestyle changes, sometimes professional help is necessary. Consider consulting a healthcare provider if:
Your hair loss is sudden or severe
You're experiencing other symptoms of hormonal imbalance (e.g., irregular periods, unexplained weight gain or loss)
You've made lifestyle changes but haven't seen improvement
You suspect an underlying medical condition
A healthcare provider can run blood tests to check your hormone levels and recommend appropriate treatments, which might include hormone replacement therapy or medications to address specific imbalances. You could also consider getting a scalp biopsy.

Hormone Havoc
Hormonal hair loss can arise from thyroid issues, menopause, PCOS, and androgenic alopecia, each affecting hair growth cycles in distinct ways.
Effective management often requires a combination of medical treatments, dietary adjustments, and stress reduction techniques.
Amidst exploring natural remedies, the guide also highlights coconut oil pulling dangers, such as the risk of aspiration leading to lipid pneumonia, jaw discomfort, and potential digestive issues.
By understanding both the complexities of hormonal hair loss and the risks associated with coconut oil pulling, individuals can make safer, more informed decisions for their health and hair care routines.
Conclusion
Hormonal hair loss causes can be complex and multifaceted, involving various hormones and bodily systems. From stress-induced cortisol spikes to the delicate balance of estrogen and testosterone, our hair health is intimately connected to our hormonal wellbeing.
Understanding these hormonal hair loss causes is the first step toward addressing the issue. By taking a holistic approach that includes diet, lifestyle modifications, and targeted interventions, it's possible to support healthy hormone levels and promote hair growth.
Remember, hair loss is often a symptom of underlying imbalances in the body. By addressing these root causes, we not only improve our hair health but our overall wellbeing. If you're struggling with hair loss, don't lose hope.
With patience, persistence, and the right approach, it's possible to nurture your hair back to health and vitality.
Previous blog
Cauliflower Wraps
Popular
08/21/2024
55.7K views
02/23/2025
46.8K views
11/18/2024
281.1K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




