Forget LDL Focus on Remnant Cholesterol
You’ve probably heard a lot about cholesterol. Your doctor talks about it. There are commercials for medication to lower it. But you may be surprised to learn there are actually different types of cholesterol.
While some types get more attention than others, they’re all part of a bigger picture. That's where understanding remnant cholesterol comes in.
When you request a cholesterol test, your results typically include measurements for various types, including total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
It's easy to walk away thinking solely about "good" HDL and "bad" LDL. However, fully grasping your heart health requires going beyond this simplified view. It means looking into a lesser-known factor: remnant cholesterol.
So, what is remnant cholesterol and why should you care?
What is Remnant Cholesterol?
Remnant cholesterol consists of leftover particles from the breakdown of certain lipoproteins called very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL). Imagine VLDL as cargo ships transporting triglycerides, a type of fat, throughout your bloodstream.
These ships make deliveries to different parts of your body, like muscles and adipose tissue.
As they unload their cargo, they become smaller and transform into remnant cholesterol particles. Think of these remnant cholesterol particles as smaller vessels carrying cholesterol remnants—leftover cholesterol and triglycerides—in your bloodstream.
This type of cholesterol is much smaller than LDL. Just like smaller vessels can still cause traffic jams, it’s important to monitor this number, too.
Why is Remnant Cholesterol Important?
While LDL cholesterol often takes center stage in discussions about heart health, remnant cholesterol has emerged as a significant player.
In fact, some studies suggest it might be even more harmful than LDL cholesterol in certain contexts. Here's why remnant cholesterol is a concern:
Artery Damage: These cholesterol remnants are small and dense. They can easily penetrate your artery walls, where they get stuck and contribute to plaque buildup.
Inflammation: Remnant cholesterol particles also tend to trigger inflammation in your blood vessels. This inflammatory response further damages the artery walls, creating an environment for plaque formation.
Heart Health Risks: All of this raises your risk of heart disease. When your arteries narrow, it becomes harder for blood to flow freely. That increases your chances of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
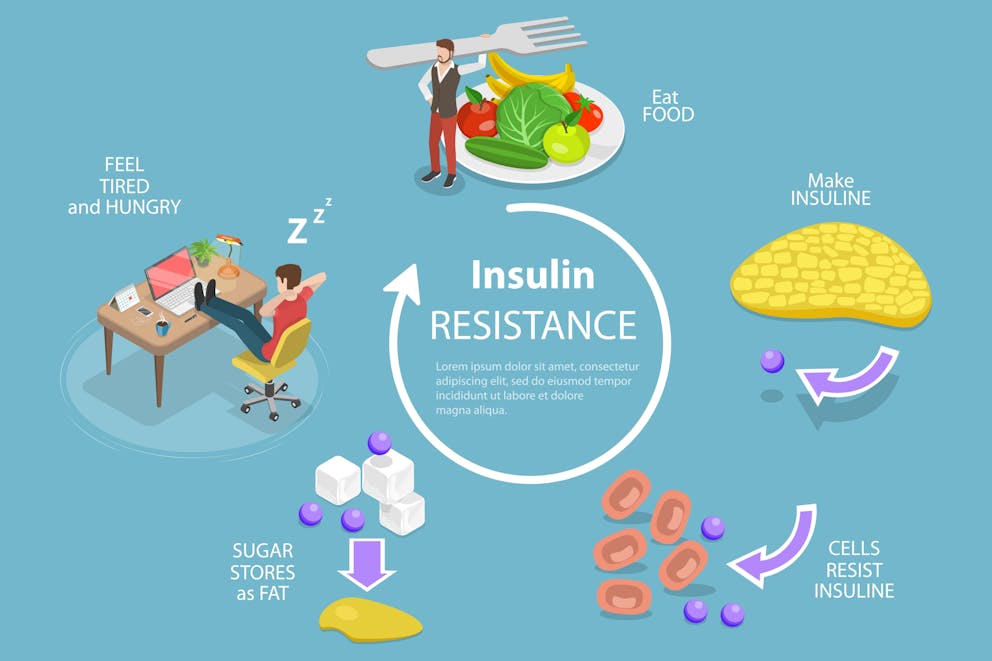
What Causes High Remnant Cholesterol?
High remnant cholesterol often stems from an imbalance in your body's fat metabolism. It’s frequently associated with insulin resistance, a condition where your body doesn't respond to insulin efficiently. Insulin resistance disrupts your body's ability to regulate sugar levels.
As a result, your liver produces more triglycerides and VLDL cholesterol. Consequently, these excess VLDL particles break down into those pesky remnant cholesterol particles, causing trouble for your heart health.
Here are some things that may contribute to high remnant cholesterol:
Diet: Diets high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats, especially trans fats, contribute to high triglycerides and increased VLDL production. Over time, these dietary habits can overwhelm your body's metabolic pathways, leading to high remnant cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle: Leading a sedentary lifestyle without regular physical activity worsens insulin resistance and elevates triglyceride levels. Exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, improving insulin sensitivity, and keeping your cholesterol levels in check. Getting your body moving can make a difference in the long run.
Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to higher triglyceride levels and may naturally have higher remnant cholesterol levels. Genetics plays a role, and if high cholesterol runs in your family, you may be more susceptible.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and hypothyroidism, increase the risk of high triglycerides. Consequently, you face high remnant cholesterol levels. Managing these conditions is crucial for minimizing the risk of elevated remnant cholesterol.
How is Remnant Cholesterol Diagnosed?
Remnant cholesterol is often excluded from a routine lipid panel. That’s why understanding remnant cholesterol and its impact on heart health is so important. To determine your remnant cholesterol level, your healthcare provider will need to look beyond your standard lipid panel.
Instead, you’ll need something called a vertical auto profile (VAP) test or an NMR LipoProfile test. These more advanced tests provide a detailed breakdown of your cholesterol particles. This gives you a clearer picture of your heart disease risk.
Many providers focus on total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides. That's why it's a good idea to engage in an open discussion with your doctor about your cholesterol.
Explain your interest in obtaining a comprehensive picture of your cholesterol profile, highlighting your desire for a remnant cholesterol measurement.
Can Remnant Cholesterol be Lowered?
The good news is, you can positively impact remnant cholesterol through diet, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, medication.
However, keep in mind that while some general strategies apply, the specifics of your approach will depend on your individual risk factors and current health status.
Start with the foundation: a healthy diet. It plays a critical role in maintaining healthy remnant cholesterol levels. The goal is to reduce your intake of refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats.
These include sugary drinks, processed foods, and foods high in saturated and trans fats.
Limit your sugar intake. Too much sugar leads to elevated triglycerides. Instead of focusing on eliminating everything enjoyable from your diet, strive for a balanced approach.
Swap out processed foods for whole, unprocessed alternatives like fruits, vegetables.
Prioritizing these foods not only reduces remnant cholesterol but also provides essential nutrients for overall well-being. You should also find ways to improve your insulin sensitivity.
Because insulin resistance plays a crucial role in developing high remnant cholesterol, incorporating lifestyle changes to combat it can be extremely beneficial. Engage in regular exercise, prioritize sleep, and consider intermittent fasting.
Even incorporating short bursts of movement into your day can help. The goal is to get your body moving and use up those stored triglycerides.

Cholesterol Clarity
Delve into the significance of remnant cholesterol, a measure of cholesterol-rich lipoproteins that can impact cardiovascular health. While LDL cholesterol is widely known, remnants refer to the cholesterol-rich particles left after the breakdown of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins.
Managing these remnants is crucial for reducing cardiovascular risk. Alongside lifestyle changes like regular exercise and a balanced diet rich in fiber and healthy fats, incorporating snacks like peanut butter fat bombs can support heart health.
These fat bombs, made from peanut butter and coconut oil, provide a tasty way to increase healthy fats and maintain a stable lipid profile.
By understanding and managing remnant cholesterol levels, individuals can take proactive steps toward better heart health and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Remnant cholesterol is an often-overlooked aspect of cholesterol management. Yet, it's emerging as a key player in heart health.
These smaller, denser cholesterol remnants can significantly contribute to plaque buildup and inflammation in the arteries, raising your risk of cardiovascular events.
Understanding how remnant cholesterol fits into the larger picture of heart health empowers you to make informed decisions. You can take proactive steps toward safeguarding your heart.
Remember, working with your doctor or a registered dietitian is key when making adjustments to your diet, lifestyle, or when considering supplements or medications to address your remnant cholesterol levels.
Previous blog
Is Ketogenic Diet Too ExtremeTags

Popular
08/21/2024
55.7K views
02/23/2025
46.8K views
11/18/2024
281.1K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




