Fasting for Fatty Liver: Benefits, Techniques & Expert Advice

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine
Fatty liver disease is caused by the buildup of excess fat in liver cells, which impairs liver function and increases the risk of liver inflammation and cancer.
Increasing evidence suggests that intermittent fasting can lower the risk of liver fat accumulation and may help reverse fatty liver disease.
Let’s look at the common causes of liver fat and how you can use fasting to fight fatty liver.
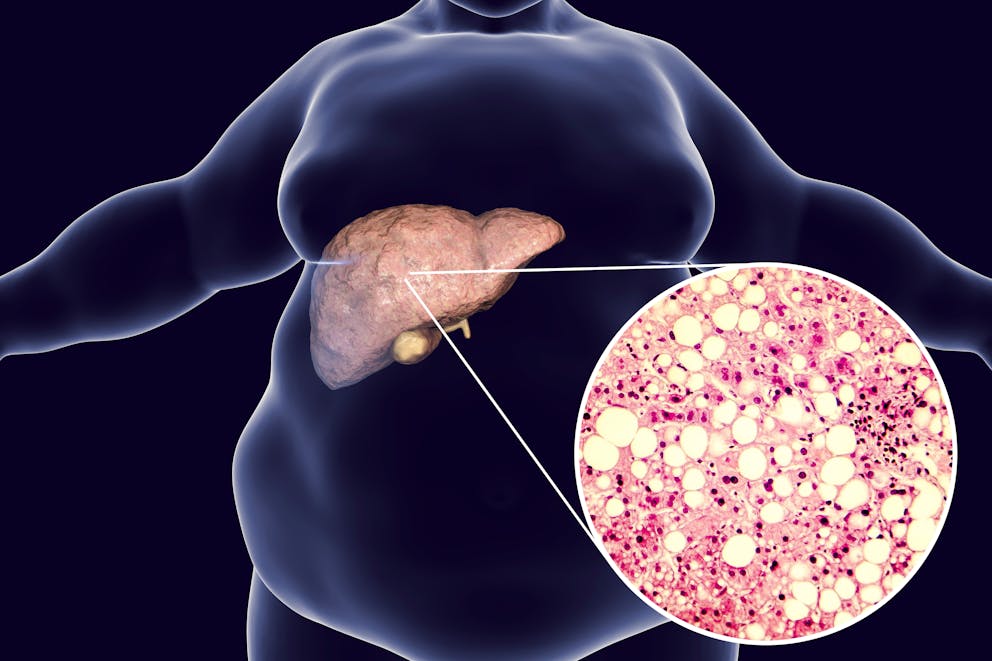
How to use intermittent fasting for fatty liver disease
Intermittent fasting is a mealtime schedule with set fasting periods followed by an eating window.
The 16:8 intermittent fast—16 hours of fasting followed by an eight-hour eating period—is a popular type of fasting that profoundly benefits liver function and supports a healthy body.
During fasting, your body burns stored fatty acids instead of blood sugar as a fuel source. This supports healthy body weight, shifts your metabolism into fat-burning mode, and triggers the production of ketones, a by-product of fat breakdown and a very efficient energy source.
To amplify the fat-burning effects of fasting and maximize liver fat reduction, it’s best to combine intermittent fasting with a low-carb ketogenic diet.
A low-carb diet like Healthy Keto® focuses on nutrient-rich foods that support steady insulin levels during the eating window, which keeps your metabolism in fat-burning mode to generate energy. This helps eliminate liver fats and promotes healthy liver function.
If you are new to intermittent fasting, it’s recommended to slowly extend your fasting periods and let your body adjust to using stored body fat as an energy source instead of sugars and carbs.
Kathy McManus, director of the Department of Nutrition at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital, advises, “Easing into an intermittent fasting plan can help your body adjust. Slowly reduce the time window for eating over a period of several months."
Combining fasting with a Healthy Keto diet is an excellent way to maintain fat burning during the eating window and support healthy nutrient levels needed to avoid fasting fatigue, headaches, or other keto flu symptoms.
Watch the video below to learn how you can use fasting to reverse fatty liver disease.
Can fasting reduce liver fat?
Evidence published in Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice suggests that fasting is beneficial for liver health, lowers the risk of fatty liver disease, and helps eliminate liver fat accumulations.
Intermittent fasting and alternate-day fasting are popular methods of meal timing that are characterized by cycling from fasting periods to periods of eating.
Because of the caloric restriction during fasting periods, the liver has to rely on stored fatty acids as an energy source and utilizes the readily available excess fat stored in liver cells first to fuel your body.
“Fasting also supports healthy insulin levels and lowers the risk of insulin resistance, a primary risk factor for developing fatty liver disease,” says Dr. Berg.
Insulin is released in response to carbs and sugar intake and regulates blood sugar. When insulin is elevated for prolonged periods, your cells become desensitized to its effects, which explains why a high-carb diet causes insulin resistance and can worsen fatty liver disease.
This study published in Frontiers in Nutrition found that individuals with NAFLD had a statistically significant reduction in liver fat in response to intermittent fasting combined with exercise compared to a control group that didn’t follow any fasting protocol and had no exercise interventions.
The same study also reported that fasting supports weight loss and fat mass reduction and has been found to improve fasting insulin levels, a marker of metabolic health linked to a lower risk of insulin resistance, diabetes, and fatty liver disease.
 What is fatty liver disease?
What is fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease is caused by fat accumulation in liver cells, which can result in liver stiffness and inflammation and can significantly increase the risk of liver cancer and cirrhosis.
Excessive liver fat can develop as a result of prolonged alcohol use, also known as alcoholic fatty liver disease. On the other hand, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) refers to fat buildup due to dietary and lifestyle habits.
Metabolic imbalances, including insulin resistance, obesity, and metabolic syndrome, are linked to developing fatty liver, and research published in the European Journal of Clinical Investigation suggests that excessive calorie consumption and a high-carb diet can significantly contribute to liver fat.
There are little to no early symptoms of fatty liver disease, and experts believe that as many as 25 percent of adults have developed excessive liver fat. Blood tests for liver enzymes, ultrasound scans, or a biopsy are typically needed to diagnose fatty liver disease.
Fatty liver disease can have serious health consequences. If you are concerned about liver fat, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine your health status and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
Key takeaways
A fatty liver can spread to all organs and typically develops due to a high-carb diet, insulin resistance, or prolonged alcohol use.
Intermittent fasting primes your metabolism to use fats instead of sugars as a fuel source which triggers the breakdown of fatty acids stored in liver cells and can help to reverse fatty liver disease.
Combining intermittent fasting with a nutritious low-carb diet like Healthy Keto supports your body’s nutritional needs while keeping your metabolism in fat-burning mode during the eating window, which maximizes the elimination of liver fat.
FAQ
1. Can fatty liver be cured by fasting?
Fasting has been found to reduce liver fat and improve fatty liver severity in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
2. Does intermittent fasting reduce your liver fat?
Yes, intermittent fasting promotes the breakdown of stored fats instead of sugars as fuel sources.
Because the liver is the main metabolic organ, it first utilizes stored fatty acids in liver cells to generate energy during fasting, which directly reduces liver fat accumulations.
3. How long should I fast for fatty liver?
A 16:8 or 20:4 fasting schedule promotes the breakdown of stored liver fat. While more extended fasting periods can amplify the fat-burning effects of fasting, it’s recommended to slowly transition into prolonged fasts to avoid fainting and other potential side effects.
4. Can fasting worsen fatty liver?
Fasting doesn’t worsen fatty liver. However, a high-carb diet can counteract the benefits of fasting, and it’s most effective to combine intermittent fasting with a low-carb ketogenic diet like Healthy Keto.
5. Can fasting help your liver?
Yes, fasting supports liver health and has been found to reduce liver fat. During periods of fasting, your liver can rest and regenerate. In addition, fasting stimulates the breakdown of fat to generate energy which reduces liver fat, lowers the risk of fatty liver disease, and promotes normal liver function.
6. Can fasting reverse liver damage?
This depends on the severity and cause of liver damage. However, liver damage due to fat accumulations can be reversed by fasting. Fasting supports liver function and stimulates the burning of liver fat as a fuel source which eliminates fat accumulation in liver cells.
7. How is the liver affected during fasting?
During fasting, the liver isn’t required to metabolize dietary fats, carbs, or proteins. This allows the liver to rest and regenerate and increases your liver's capacity to detoxify metabolic by-products, hormones, and harmful environmental toxins.
In addition, the liver breaks down stored fats during fasting periods to generate energy, reducing liver fat and supporting healthy liver cell function.
8. Can prolonged fasts help a fatty liver?
Yes, prolonged fasts can help a fatty liver. The longer the fasting period, the more body fat is broken down and used as an energy source.
However, it’s recommended to slowly transition into extended fasting periods to avoid fainting or other side effects of prolonged caloric restriction.
9. What should I drink in the morning for fatty liver?
Drinking a glass of apple cider vinegar and lemon water in the morning is an excellent choice to eliminate liver fat and lower the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
Apple cider vinegar and fresh lemon juice support liver function, protect liver cells from the adverse effects of detoxification, and can prevent fat accumulation in the liver.
10. Does fasting detox the liver?
Yes. Fasting helps the liver to rest, which increases its capacity to detoxify. In addition, research suggests that fasting promotes the production of liver enzymes that play a crucial role in detoxification and support the elimination of metabolic by-products and toxins.
Previous blog
Copper Toxicity: Symptoms, Causes, and What to Do
Popular
08/21/2024
55K views
02/23/2025
46.3K views
11/18/2024
277.5K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




