What Causes Sludge in Gallbladder? Get Rid of Bile Sludge Fast

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns
Bile that becomes too thick and overly concentrated can form gallbladder sludge linked to upper abdominal pain, digestive issues, gallstones, and gallbladder inflammation.
Discover what causes sludge in the gallbladder and learn how taking bile salts and making the right dietary choices can help get rid of bile sludge fast.
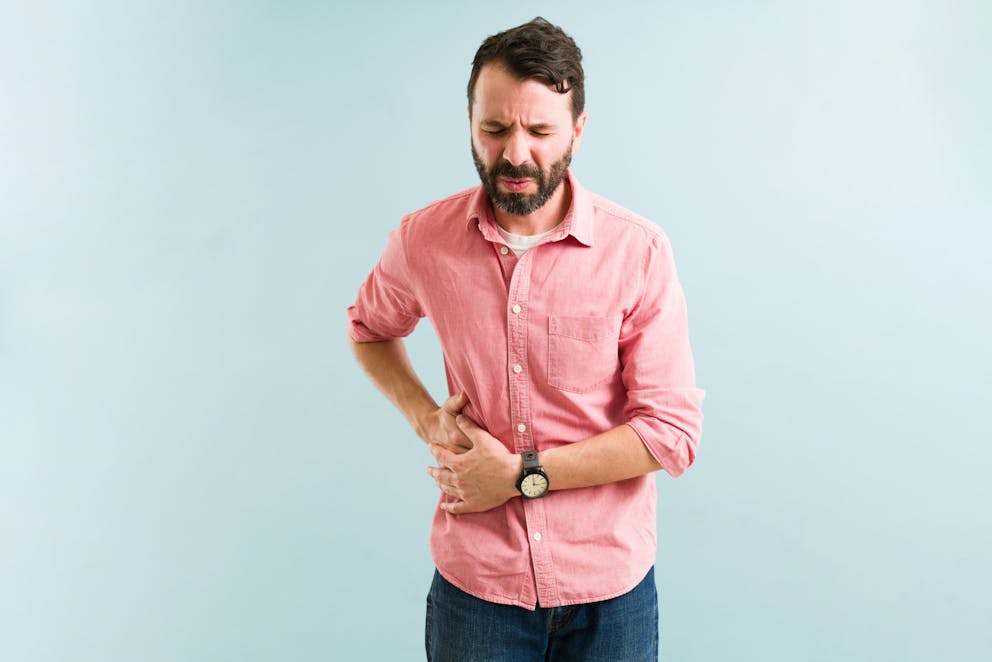

What is bile sludge?
Bile sludge, also called gallbladder or biliary sludge, forms when bile becomes thick and highly concentrated.
Bile is a vitally important fluid produced by liver cells and stored in the gallbladder. It plays a crucial role in digestion, absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, normal liver function, and the detoxification of drugs, heavy metals, and metabolic by-products.
Bile is a combination of cholesterol crystals, bilirubin, calcium salts, and mucins and contains bile salts, which act as a natural thinning agent that keeps bile soluble.
“Low bile salt production can lead to bile sludge, which significantly lowers the rate of bile flow into the small intestines,” explains Dr. Berg. “This can result in digestive issues, the formation of gallstones, and may lead to gallbladder inflammation.”
Watch the video below to learn about the most effective gallbladder sludge treatment.
Symptoms of bile sludge
Bile sludge can obstruct the bile duct system, causing a back-up of bile into the liver and gallbladder, leading to poor digestion, gallbladder and liver problems, chronic pain, and inflammation.
Here are common symptoms of bile sludge:
Abdominal pressure
Pain in the upper right shoulder, chest, or abdomen
Difficulty digesting fatty foods
Poor detoxification
Chest pain
Vomiting and nausea
Fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies
Fatigue
Bile sludge can cause an inflamed gallbladder, or acute cholecystitis, which may require gallbladder removal surgery in severe cases.Blocked bile ducts can also impair normal liver function, contribute to the development of cirrhosis, and weaken the liver's immune defenses, significantly increasing the risk of hepatitis.
If you experience symptoms indicative of bile sludge, it’s essential to consult with a medical professional to evaluate your gallbladder function and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
A thorough medical history, blood tests, and liver function tests can help diagnose bile sludge, gallbladder stones, and gallbladder disease.
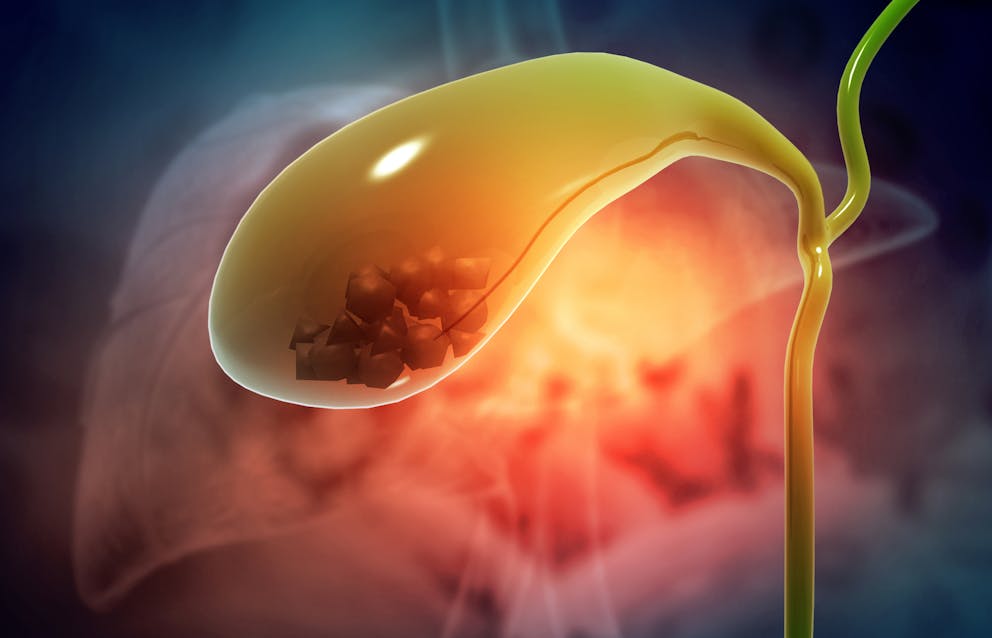
What causes sludge in your gallbladder?
Gallbladder sludge can have various causes and is often triggered by a combination of dietary factors, liver issues, a sluggish gallbladder, and hormonal imbalances.
Poor liver function, fatty liver disease, and a low-fat diet can lead to low bile flow, which causes saturated bile and increases the risk of developing sludge. In addition, research published in Gut found that elevated insulin levels—a result of a high-carb diet—can impair gallbladder muscle contraction linked to gallbladder sludge.
Other risk factors of bile sludge include:
Pregnancy
Rapid weight loss
Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy
History of taking antibiotics
Gastric bypass surgery
Prolonged and intermittent fasting can increase the risk of gallbladder sludge in some individuals. However, this often is a temporary issue that goes away once the body adapts to fasting.
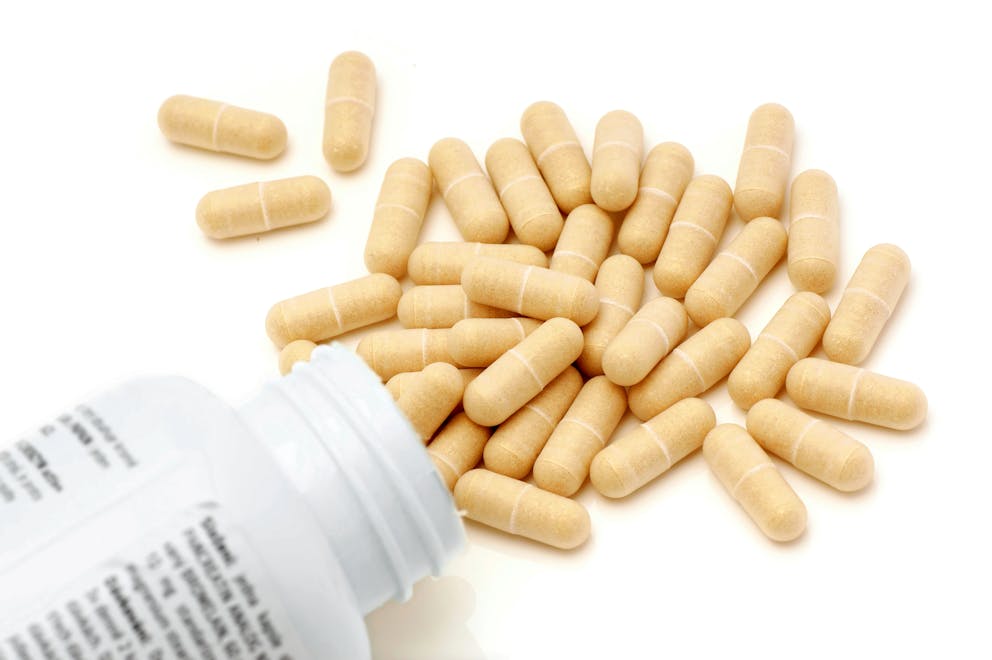
How to get rid of bile sludge
Bile sludge can impair the digestive process, contribute to gallbladder inflammation, and turn into gallstones. Understanding how to increase bile is crucial to support your digestive health and prevent gallbladder sludge.
Here are three steps that you can take to promote normal bile flow.
1. Take purified bile salts
Purified biliary salts are emulsifying agents that keep bile soluble and lower the risk of sludge formation and gallbladder stones.
Taking a purified bile salt supplement helps promote healthy bile flow and supports digestion and the elimination of toxins.
Ox bile benefits extend beyond just aiding digestion and nutrient absorption. Bile salts are especially beneficial for individuals with fatty liver disease and those who had their gallbladder removed.
It’s recommended to take purified bile salts on an empty stomach to dilute gallbladder sludge and clear potential blockages in the small ducts connecting the liver, gallbladder, and intestinal tract.
2. Increase choline-rich foods
Choline is an essential nutrient that stimulates bile flow and promotes gallbladder health.
Choline is converted into acetylcholine, a vital neurotransmitter released by the nerves of the digestive system that regulates gallbladder muscle contractions and bile flow into the small intestine.
This is confirmed by a report published by the National Institute of Health stating that choline-rich foods, including cruciferous vegetables, artichokes, beet tops, egg yolks, and ginger, support bile production and normal bile flow.
Choline can also be taken as a supplement to promote gallbladder health and speed up digestion after eating fatty foods.
3. Support a diverse gut flora
The gut is populated by billions of beneficial microorganisms that play an essential role in immune defenses, nutrient absorption, and the recycling of bile salts.
Antibiotics, alcohol consumption, and a diet high in processed foods can impact the diversity of the microflora and lead to the overgrowth of potentially harmful microbes, also known as dysbiosis.
Research published in Current Gastroenterology Reports found that dysbiosis is directly linked to a reduced rate of bile acid recycling and inadequate bile salt concentrations.
Consuming plenty of probiotic and prebiotic foods, avoiding processed foods, and limiting alcohol promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and normal bile salt concentrations.
4. Avoid a low-fat diet
Bile fluid is released when dietary fats enter the small intestines, and a low-fat diet can cause a lack of sufficient gallbladder muscle contraction, potentially contributing to gallbladder sludge.
While it may sound counterintuitive, the higher the fat content in meat, the more easily it can be digested. Fat triggers bile release and slows down digestion, which allows bile salts and digestive enzymes to fully break down and digest fat-containing foods.

Key takeaways
Understanding what causes sludge in the gallbladder is crucial to get rid of bile sludge fast.
Saturated bile often develops due to a combination of dietary choices, hormonal imbalances, poor gallbladder function, and potential liver problems.
Taking purified bile salts, supporting a healthy microflora, and increasing your intake of choline-rich foods can promote normal bile flow and may help to prevent or reverse bile sludge.
FAQ
1. What does gallbladder sludge indicate?
Gallbladder sludge typically indicates a lack of adequate bile salts needed to keep bile soluble or may be a sign of sluggish gallbladder function or liver issues.
2. Can gallbladder sludge cause pancreatitis?
Yes, gallbladder sludge can increase the risk of developing acute pancreatitis.
Bile sludge can obstruct the small ducts connecting the gallbladder, pancreas, and liver to the small intestines. This can trap digestive enzymes in the pancreas, leading to irritation, inflammation, and the development of pancreatitis.
3. What are the first signs of gallbladder sludge?
Poor digestion, abdominal pressure or pain, indigestion, nausea, pale-colored stool, and bloating are common early warning signs of gallbladder sludge.
4. What causes the formation of biliary sludge?
Biliary sludge is typically a result of low bile salt concentrations causing saturated bile fluid with a thick consistency, which significantly increases the risk of gallstones.
5. Can dehydration cause gallbladder sludge?
Yes, dehydration can potentially contribute to gallbladder sludge. Bile is a digestive fluid that contains water, and adequate hydration helps to maintain the fluidity of bile, preventing it from becoming overly concentrated.
6. Can gallbladder sludge cause inflammation?
Yes. Bile sludge can block the duct that allows bile to flow into the intestines. This can cause an accumulation of bile sludge in the gallbladder and trigger gallbladder inflammation, also known as acute cholecystitis.
7. How do you get rid of gallbladder sludge?
Purified bile salts are a convenient and effective way to keep bile soluble, which can help prevent or treat gallbladder sludge. In addition, increasing choline-rich foods such as ginger, beet tops, artichokes, and egg yolks promote gallbladder function and support normal bile flow.
8. Can gallbladder sludge cause fatigue?
Yes. Gallbladder sludge can impair the detoxification of drugs, metabolic by-products, and heavy metals, and a build-up of toxins within the liver can interfere with metabolic processes and result in fatigue.
9. Can bile sludge turn into gallstones?
Yes, bile sludge is a primary cause of gallstones. Because the gallbladder stores bile, sludge can become saturated and crystallize, leading to the formation of gallstones.
10. Does gallbladder sludge require surgery?
Gallbladder sludge doesn’t typically require surgery. However, if left untreated, bile sludge can cause gallstones, pancreatitis, and inflammation of the gallbladder, which may require gallbladder removal.
Previous blog
Key Points on Yearly CheckupsNext blog
On a Statin WATCH THISTags

Popular
08/21/2024
55K views
02/23/2025
46.3K views
11/18/2024
277.5K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




