What Are the Best Probiotics for Diabetes? (Type 1 and Type 2)

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved

Healthy Keto Acceptable Foods List
Explore a comprehensive list of foods and beverages that align with Healthy Keto®
Identify which foods support fat-burning and metabolic health
Discover nutritious options for fats, proteins, and vegetables to support your health goals
Learn about common foods that aren’t Healthy Keto-approved
It’s well known that probiotics promote gut health and strengthen the immune system. But did you know that certain probiotic bacteria promote metabolic health and may benefit diabetes management?
Let's look at the connection between beneficial gut bacteria and blood sugar control and discover the best probiotic for diabetes.
What are probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms such as bacteria and yeasts that naturally reside in the human digestive system and contribute to the formation of the gut microbiome.
A healthy gut microbiome is crucial for immune system and digestive tract function and supports overall health and well-being.
Beneficial bacteria promote microbial diversity in the gut, which helps prevent the overgrowth of potentially harmful microbes linked to various health issues.
Factors such as frequent antibiotic use, regular alcohol consumption, chronic stress, and a diet high in sugar and processed foods can negatively impact microbial diversity, leaving many at risk of an imbalanced microflora.
A study published in the Canadian Family Physician reports that an imbalanced gut microbiome is associated with an increased risk of gastrointestinal issues, poor immune defenses, food allergies, depression, and skin conditions.
Watch the video below to learn how beneficial dietary choices can help manage diabetes.
What Would I Eat if I had Diabetes?
What Would I Eat if I had Diabetes?
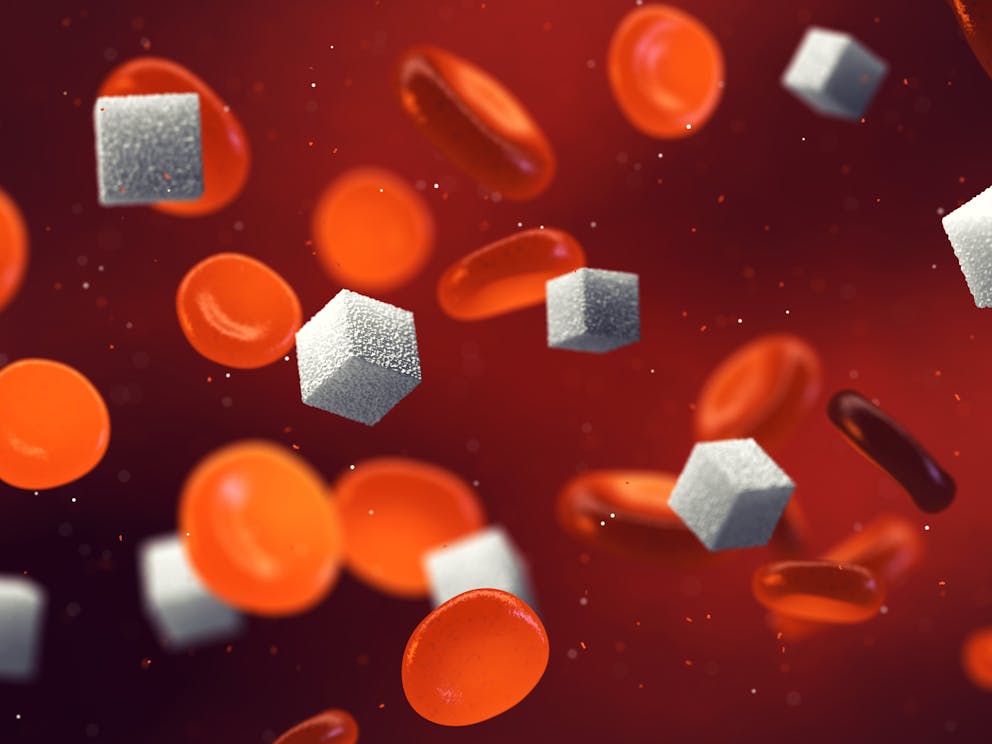
Benefits of probiotics for diabetes
Increasingly more research suggests that probiotics may have potential benefits for diabetes management.
A study published in Nature reports that lack of microbial diversity can contribute to chronically elevated blood sugar levels and insulin resistance—the leading causes of type 2 diabetes.
“Beneficial gut bacteria can impact the regulation of blood glucose levels and insulin secretion,” explains Dr. Berg. “Promoting a healthy gut microbiome with probiotics has the potential to improve blood sugar control and diabetes.”
Check out these five benefits of probiotics for diabetes.
1. Improved insulin sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a metabolic disorder characterized by cellular unresponsiveness to insulin, a critical metabolic hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels.
A diet high in sugars and carbohydrates can lead to frequent blood sugar spikes and the gradual loss of cellular sensitivity to insulin, which is linked to elevated blood sugar levels and the development of diabetes.
A study published in Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome found that probiotic bacteria can enhance the insulin sensitivity of muscle and liver cells, which promotes healthy insulin levels, lowers the risk of insulin resistance, and supports balanced blood sugar levels.
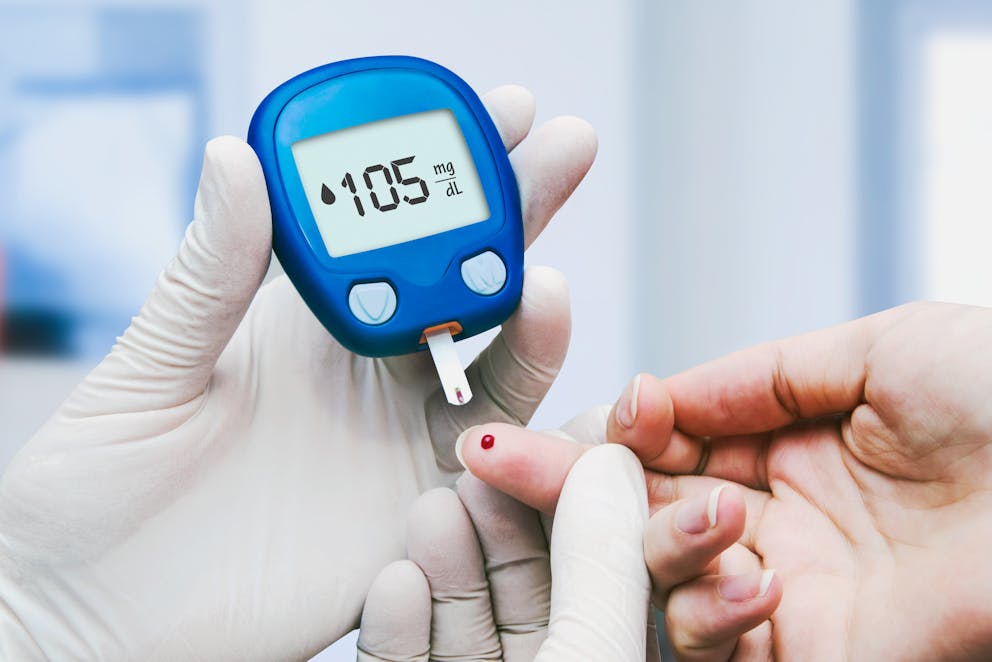
2. Enhanced blood sugar control
Probiotic microbes ferment various types of prebiotic fiber in the colon, which releases short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
SCFAs promote insulin sensitivity and improve glucose tolerance, a measure of the body’s ability to control blood sugar levels after a carbohydrate-containing meal.
A study published in Advances in Nutrition investigated the health benefits of probiotics for diabetes and concluded, “Probiotics have a beneficial effect on fasting plasma glucose in adults with type 2 diabetes and benefit glycemic control in prediabetic individuals.”
3. Lower risk of type 1 diabetes
While type 2 diabetes typically is a result of dietary and lifestyle habits, type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Beneficial gut bacteria interact with various immune cells and promote balanced immune responses associated with a lower risk of autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes.
In addition, a diverse gut microbiota enhances the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, which can benefit individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Research published in Microorganisms investigated the effects of probiotics in people with type 1 diabetes and concluded that probiotic supplementation is associated with better glycemic control and improved metabolic health.
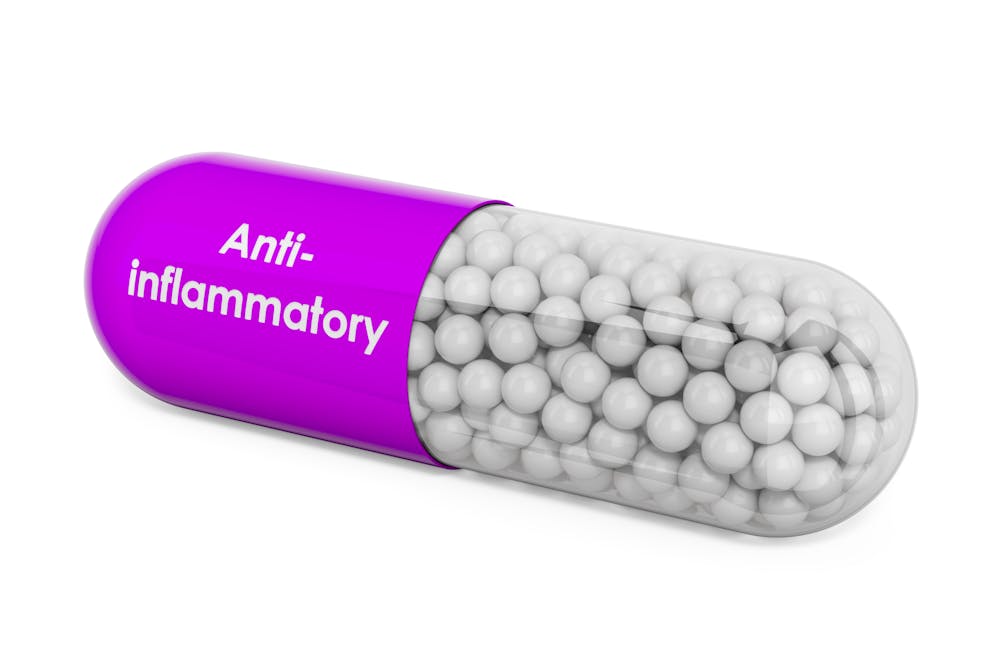
4. Anti-inflammatory
Chronic inflammation plays a central role in metabolic diseases, including diabetes.
Inflammation contributes to insulin resistance and can trigger hormone imbalances linked to poor blood sugar control.
Probiotics can reduce inflammation by modulating the immune system and generating anti-inflammatory SCFAs, which are linked to better metabolic health and a lower risk of diabetes.
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of probiotic bacteria may also help mitigate some long-term consequences of diabetes, including:
Vascular inflammation
Diabetic retinopathy
Increased risk of heart disease
5. May benefit diabetes-related gastroparesis
Diabetes increases the risk of gastroparesis, a condition characterized by delayed emptying of the stomach, which can lead to digestive issues, including nausea, heartburn, and bloating.
Probiotics promote normal digestive function, and research published in Microorganisms found that Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus plantarum appear especially beneficial for managing gastroparesis.
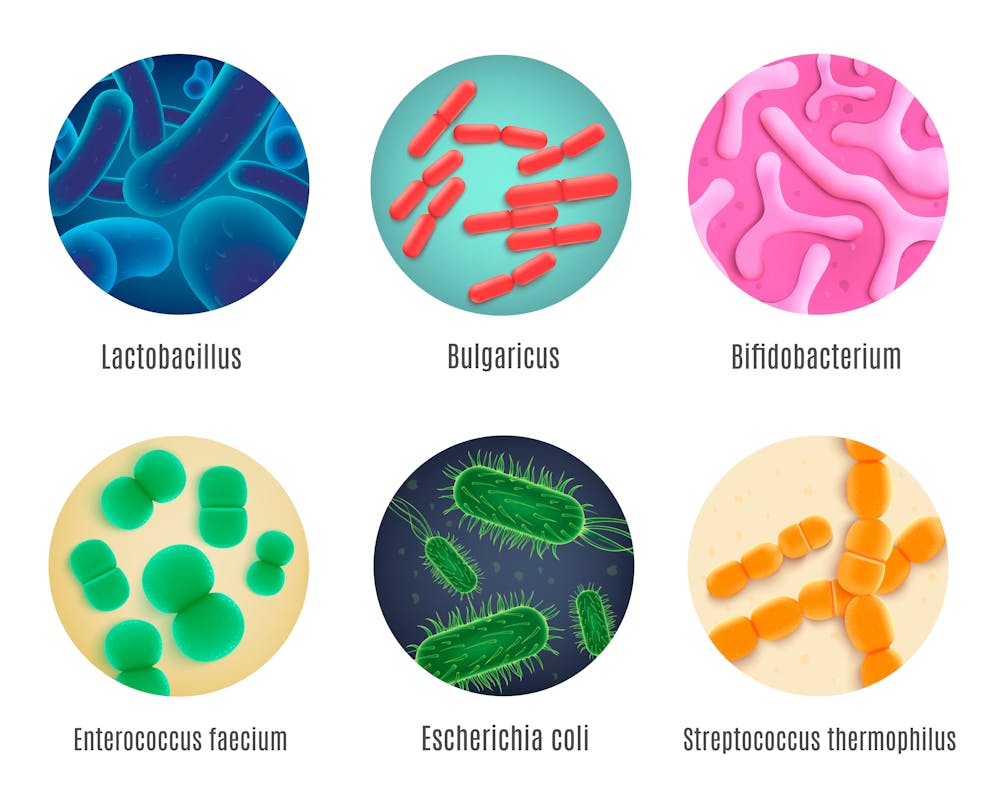
What are the best probiotics for diabetes?
The human microflora contains around 500 different types of probiotic species, and the number of life bacteria in the gut is greater than ten times that of all human cells in the body.
However, not all probiotics provide the same health benefits, and more research is being conducted to determine which bacterial strains may help manage diabetes most effectively.
Top probiotic strains for type 2 diabetes
Specific strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have demonstrated the potential to stabilize blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote metabolic health.
Here are the best probiotics for type 2 diabetes:
Lactobacillus acidophilus
Lactobacillus bulgaricus
Lactobacillus casei
Bifidobacterium lactis
Bifidobacterium breve
Bifidobacterium longum
To augment the health benefits of these probiotics for diabetes, it’s recommended to take a high-quality probiotic supplement comprising most or all of these bacterial strains.
It’s equally important to opt for a product that contains at least 60 billion colony-forming units (CFU) per serving.
CFU indicates the number of live bacteria in the product, and dietary supplements with fewer than 60 billion CFUs may not deliver adequate amounts of microbes into the gut.
Top probiotic strains for type 1 diabetes
While more research is needed to establish the link between probiotics and a lower risk of autoimmune diabetes, certain bacteria have been found to promote blood sugar control in individuals with type 1 diabetes.
These probiotic strains have shown potential benefits for type 1 diabetes:
Bifidobacterium lactis
Bifidobacterium breve
Bifidobacterium longum
Lactobacillus casei
Lactobacillus plantarum
Lactobacillus acidophilus
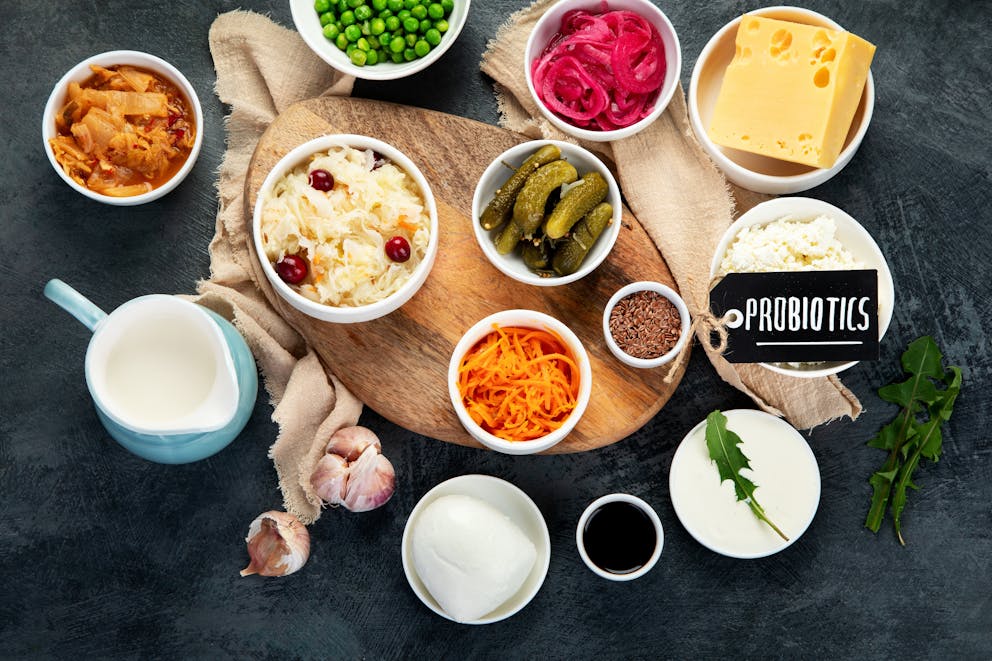

Sources of probiotics
Probiotics can naturally be obtained from probiotic-rich foods or taken as probiotic supplements.
You may have heard that yogurt and kefir are the best dietary sources of probiotics. While these foods contain good bacteria, they’re not the best probiotic foods.
Fermentation creates an ideal environment for probiotics to thrive, making fermented vegetable products some of the top natural sources of probiotics.
Here are some of the best probiotic-rich foods:
Consuming plenty of probiotic-rich foods helps increase your gut bacteria diversity and promotes a healthy microbiome.
However, many individuals don’t consume enough fermented foods to support a balanced gut microflora, and probiotic supplements offer a safe and effective alternative to probiotic foods.
Probiotics are widely available as capsules, tablets, and powders, and liquid probiotics are becoming an increasingly popular option for those who prefer not to swallow pills or capsules.
Risks and precautions
Probiotics are generally well tolerated and associated with minimal risks and side effects.
Some probiotic supplements or fermented foods can contain carbohydrates, and it’s crucial that individuals with diabetes opt for carbohydrate-free probiotic sources to avoid blood sugar spikes.
In some cases, probiotic supplements can cause gastrointestinal issues such as gas bloating or abdominal pain. These side effects are generally mild and transient and typically resolve with continued use of probiotics.
However, if you experience prolonged or intense gastrointestinal discomfort following the use of probiotics, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive assessment of your symptoms.

Key takeaways
Evidence suggests that certain strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium are the best probiotics for diabetes.
These probiotic bacteria may help improve insulin sensitivity, stabilize blood sugar levels, and mitigate the health consequences of diabetes, including diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular damage.
Additional Probiotics Resources
FAQ
1. What is the best probiotic for diabetes?
Evidence suggests that Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Lactobacillus casei, Bifidobacterium lactis, Bifidobacterium breve, and Bifidobacterium longum are the best probiotics for diabetes.
2. How do probiotics help with diabetes?
Probiotics promote a healthy microbiome, which has various beneficial effects on metabolic health and immune function and is linked to a lower risk of type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Certain probiotics have been found to improve insulin resistance, enhance glucose tolerance, and lower inflammation, all of which are crucial factors for preventing and managing diabetes.
3. Which probiotic food is best for diabetes?
Fermented foods low in carbohydrates—including miso, sauerkraut, kimchi, and natto—are some of the best natural sources of beneficial bacteria for diabetes.
In addition, prebiotic foods such as asparagus, onion, garlic, and artichoke provide fuel and nutrients for beneficial gut microbes and can help maximize the health benefits of probiotics for diabetes.
4. Should diabetics take probiotics?
Yes, people with diabetes may benefit from taking probiotics.
Evidence suggests that certain probiotic strains of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus can improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in diabetic individuals.
5. What probiotic lowers A1C?
Probiotic strains, including Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, and Bifidobacterium lactis, have been linked to improved blood sugar control and lower A1C levels.
6. What probiotics are good for lowering blood sugar?
Probiotic supplements containing different strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium can help enhance cellular insulin sensitivity, which is vital to lower blood sugar levels.
7. Is it safe to take probiotic supplements if I have diabetes?
Yes, probiotics are generally considered safe for individuals with diabetes.
However, some probiotic supplements can contain carbohydrates, and opting for a carb-free probiotic supplement is crucial to avoid blood sugar imbalances.
8. What are the side effects of taking probiotics for diabetes?
While probiotics have minimal side effects, some individuals can experience mild and transient gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain.
These side effects are linked to changes in microbial diversity and typically improve within a few days of continued probiotic use.
9. Can probiotics help manage type 1 diabetes?
Evidence suggests probiotics can enhance blood sugar regulation and may help manage type 1 diabetes.
In addition, probiotics interact with immune cells and promote balanced immune responses, which have been linked to a lower risk of autoimmune conditions, including type 1 diabetes.
10. Can probiotics help improve insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes?
Probiotics ferment prebiotic fibers into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have been found to improve insulin sensitivity in diabetic individuals.
Sources
Previous blog
4 Benefits of Oral Probiotics – And How To Use ThemTags

Popular
08/21/2024
55.7K views
02/23/2025
46.8K views
11/18/2024
281K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




