Hormone Imbalance: Signs, Causes, and Solutions
Hormone imbalance can be detrimental to your physical and mental health. It can happen when glands produce too much or too little of any hormone—often caused by lifestyle changes, unhealthy diets, stress, and aging. Learn about the telltale signs of irregular hormones and how you can balance them naturally.

What are hormones?
Hormones are chemical messages sent through your bloodstream from your endocrine glands to your cells. Cells have receptors that receive hormones—triggering certain functions within the cell.
Imagine yourself speaking into a microphone to a crowd of people. You are doing the job of an endocrine gland—your voice is transmitting information (hormones), and the audience members (receptors) are listening to and receiving the information, which they can act on.
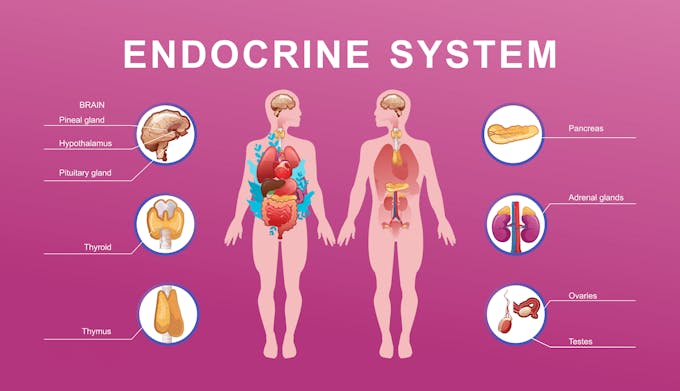
Your body has eight primary endocrine glands that produce hormones and regulate your body functions. Insulin and glucagon are hormones secreted by the pancreas, which instruct your body to regulate its blood sugar level. Insulin lowers your sugar level when it's too high, and glucagon increases it when it’s too low. If either or both of these hormones don’t function properly, you risk having diabetes.
Hormone cheat sheet
In the same way insulin deficiency causes diabetes, other hormone-related conditions can also cause health complications.
Learn more about your key hormones, their secreting glands, and their functions.
Adrenaline
Secreting gland: Adrenals
Functions: Increases heart rate, blood flow and pressure, and metabolism in response to stress
Cortisol
Secreting gland: Adrenals
Function: Helps the body adapt to stressors
Aldosterone
Secreting gland: Adrenals
Functions: Regulates water and salt balance
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S)
Secreting gland: Adrenals
Functions: Causes body odor production and hair growth during puberty
Estrogen
Secreting gland: Ovaries
Functions: Maintains pregnancy, regulates the menstrual cycle, and develops female sex function
Progesterone
Secreting gland: Ovaries
Function: Prepares the body for pregnancy after egg fertilization
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Secreting gland: Pituitary
Functions: Controls egg and sperm production
Luteinizing hormone
Secreting gland: Pituitary
Functions: Controls ovulation, estrogen, and progesterone production
Prolactin
Secreting gland: Pituitary
Function: Aids breast milk production
Oxytocin
Secreting gland: Pituitary
Functions: Assists childbirth, lactation, and mother-child bonding
Melatonin
Secreting gland: Pineal
Function: Regulates the sleep-wake cycle
Parathyroid hormone
Secreting gland: Parathyroid
Function: Controls calcium levels
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Secreting gland: Pituitary
Functions: Controls energy levels and metabolic rate
Testosterone
Secreting glands: Ovaries, testes, and adrenals
Functions: Promotes sex drive in males and females and develops male sex characteristics
What is hormonal imbalance?
Hormonal imbalance occurs when you have too much or too little of one or more hormones, often due to external factors restricting their function. Disease, exposure to endocrine disruptors, and poor diet and lifestyle choices are common causes of hormone imbalance and abnormal hormone function.
Hormone imbalance can be gender-specific or age-specific. It can also occur temporarily due to natural events, including pregnancy, breastfeeding, childbearing, menopause, and aging.

Signs of hormone imbalance
Since there are over fifty hormones in our endocrine system, it can be difficult to tell which hormones are out of balance. Consequences of high estrogen in men include increased risk of cardiovascular issues, enlarged prostate, and stroke to name a few. Here are common signs of hormone imbalances in men and women.
Hormonal imbalance symptoms in women:
Acne
Hot flashes
Heavy periods
Mood swings
Brain fog
Poor sleep
Unexplained weight gain or weight loss
Low libido
Infertility
Constipation or diarrhea
Irregular periods
Abdominal pain
Anxiety
Brittle bones
Excess hair growth
Rashes
Headaches
Fatigue
Hormonal imbalance symptoms in males:
Hyperthyroidism
Low libido
Unexplained weight gain or weight loss
Erectile dysfunction
Hair loss
Chest tenderness
Note: Other medical conditions can trigger these signs too, so take a blood test to confirm your hormone levels.

What causes hormone imbalance?
Here are the five most common causes of hormone imbalance.
1. Stress
Stress is the most common cause of hormone imbalance. It activates the release of adrenal hormones, including cortisol and adrenaline. Cortisol allows you to adapt to physical and mental stressors, while adrenaline prepares your body for fight or flight when you face danger.
Cortisol imbalance can disrupt your endocrine system because it affects the production of other adrenal hormones, sex hormones, and growth hormone. Growth hormone opposes cortisol—when your cortisol level is high, your growth hormone level decreases.
Too much stress can also cause adrenal fatigue syndrome. This is when your adrenal glands are so overworked that they can no longer secrete enough cortisol needed for your endocrine system to function properly.
Another hormone affected by high cortisol levels is progesterone, which controls the menstrual cycle and fertility. Progesterone is a precursor to cortisol, and it decreases when you’re stressed.
2. High-carb diets
Each time you consume high-carb foods like rice or bread, you trigger insulin. The pancreas gland secretes insulin to convert carbohydrates to glucose, which is then stored as glycogen in the liver.
High-carb diets will cause your pancreas to produce too much insulin, which can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is when your insulin receptors become resistant or "numb" to insulin.
Insulin resistance increases the risk of women-specific health conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)—a hormonal disorder that causes enlarged ovaries with cysts on the edges.
High-carb diets can also lead to an underactive thyroid and estrogen dominance.
3. Menopause
Menopause is the natural decline of reproductive hormones. It’s age-related, and many women notice symptoms as they reach their 40s or 50s. Menopause is diagnosed after going 12 months without a menstrual period.
During this natural transition, the ovaries stop producing estrogen and progesterone. Because of this, other hormones like LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) are elevated.
Some menopausal symptoms related to high LH and FSH include mood swings, hot flashes, vaginal dryness, weight gain, and frequent urinary tract infections.
4. Autoimmunity
Autoimmunity is when your immune system attacks healthy cells instead of microbial infections. Autoimmune conditions damage your body's tissues and hormone-secreting glands.
There are over a hundred known autoimmune conditions with unknown causes to date. However, some have been traced to environmental or genetic factors.
For example, Addison’s disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the function of the adrenal glands. Common signs of Addison’s disease include fatigue, weight loss, low appetite, nausea, and other metabolic disorders.
5. Birth control
Birth control pills can act as endocrine disruptors, interfering with the hormone process that’s essential for ovulation.
Many birth-control pills are known to contain synthetic estrogen and progesterone. These synthetic hormones can throw off your hormone levels and cause an imbalance.

Conditions caused by hormone imbalance
Hormonal imbalance can lead to various health conditions—here are the most common.
Diabetes
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are caused by abnormal insulin levels. Excess insulin secretion (hyperglycemia) is associated with type 2 diabetes, while low insulin secretion (hypoglycemia) is associated with type 1 diabetes.
Estrogen and progesterone are other hormones that affect the body’s response to insulin. During menopause, insulin levels can fluctuate drastically and can lead to diabetes.
Obesity
Obesity is linked to abnormal insulin, leptin, somatropin, and sex hormone levels. When your body is insulin resistant, you gain weight due to the storage of excess body fat.
Sex hormones can also impact fat distribution. Women tend to store fat in their lower abdomen during their childbearing years. As aging men and women develop hormone imbalances, they store fat around the abdomen.
Leptin is another hormone that controls how your body stores fat. It’s common to see high levels of this hormone in obese people who tend not to feel full after eating.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormone disorder that affects the female reproductive system. It causes the development of follicles in the ovary, which hinder the production of eggs.
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown but has been traced to insulin resistance. Some common symptoms of PCOS include irregular periods, elevated androgen levels, and enlarged ovaries.
Acne
Acne is a skin condition triggered by high androgen levels in the body, especially testosterone. High testosterone levels increase the production of sebum, an oily substance secreted at the base of the hair meant to protect and lubricate the skin.
The oversecretion of sebum will block the hair pores and attract bacteria, leading to inflammation. This is why male teenagers experience pimples during puberty—they have high testosterone levels at this stage.

How to balance your hormones
It’s crucial to correct your hormone imbalance to avoid further health complications and support your overall well-being. Use these seven natural and effective ways to promote balanced hormones.
1. Keto
The ketogenic diet plays a major role in balancing hormones. Because keto is a low-carb diet, it helps lower insulin levels and promote insulin sensitivity, making insulin more effective.
The healthy fats included in the keto diet help improve steroid hormone levels, including testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, cortisol, and aldosterone.
The keto diet has been known to balance androgen levels in women and increase testosterone levels in men. Keto also supports adrenal function, giving you a greater sense of calmness. Having a healthy keto diet plan is tremendously helpful in getting your hormones on track.
2. Intermittent fasting
Intermittent fasting involves fasting outside of an eating window on a regular schedule. A great example would be eighteen hours of fasting followed by a six-hour window where you can eat keto-friendly foods.
Your insulin can’t be triggered if you’re not eating. Because intermittent fasting reduces insulin, it also reduces the risk of insulin resistance and improves insulin sensitivity.
Cortisol (the fight or flight hormone) is another stress hormone improved by fasting. While fasting, cortisol activates lipase, which makes losing weight easier.
3. Quality foods
What you eat greatly impacts your hormone levels. Avoid non-organic foods that contain endocrine disruptors, like pesticides, herbicides, GMOs, and synthetic hormones. Instead, consume foods rich in vitamins and minerals to support your hormone health.
You can also use nutrients to influence your hormone balance. Cruciferous vegetables, like cabbage, inhibit iodine, which makes them great for supporting an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). Seafood like fish and crab are great sources of selenium, which is essential for converting T4 (thyroid hormone) to T3 (an active form of your thyroid hormone).
Foods rich in arginine, like eggs and seafood, can help improve your growth hormone, insulin, glucagon, and peptide hormone levels. Red meat, oysters, and nuts which are high in zinc, help balance your testosterone levels, and cortisol is influenced by potassium and calcium-rich foods.
Low-carb diets help regulate your insulin and androgen levels. To help support your endocrine system and promote hormonal health, try the Healthy KetoTM diet and an intermittent fasting plan.
4. Nutritional supplements
Nutritional supplements containing essential vitamins and minerals also help with balancing hormones. Nutritional yeast supplements are excellent for hormone balance. They contain trace minerals, amino acids, and B vitamins.
Diindolylmethane (DIM) is another supplement to try. It’s a phytonutrient found in cruciferous vegetables. DIM helps estrogen imbalance by converting excess androgen to estrogen. So, if you have androgen dominance symptoms as a woman, try DIM.
5. Lower stress
Stress affects your hormone levels in many ways. The cortisol hormone allows you to cope with stress. So, reducing your stress level is an effective way to help this hormone.
Chronic stress will elevate your cortisol level, which stimulates your appetite and intake of carbohydrate foods. When your carbohydrate intake increases, your insulin hormone level will rise too. A high insulin level can cause insulin resistance. So, reducing stress will simultaneously improve your cortisol and insulin levels.
6. Exercise
Exercise will help you manage your stress level, but you shouldn't overdo it. Overtraining can give you the opposite results you’re looking for—causing your body more harm than good.
After intense exercise, your body needs to rest. This rest will help you achieve more benefits from your workout and will also help balance cortisol.
High-intensity exercise can cause a spike in growth hormone. One study showed that exercise improves insulin sensitivity, and even has a positive effect on your testosterone levels.
7. Quality sleep
Sleep is essential for many areas of your health. Getting quality sleep regulates certain hormones like your thyroid hormone, growth hormone, cortisol, estrogen, and hormones that increase appetite.
Poor sleep can lead to high thyroid hormone levels. Hunger hormones like leptin, insulin, and ghrelin are also regulated by sleep, which is why you have more cravings after a night of poor sleep.
Getting plenty of high-quality sleep can be a natural hormone therapy because it influences your hormone balance and helps reduce cravings for unhealthy foods.
![]()
Key takeaways
Hormones are chemical messages that control your body's functions. Hormonal imbalance is when the hormone level is too high or too low. Many hormones in the body can be triggered by nutrition, stress, menopause, high-carb diets, and birth-control pills.
Some ways to improve your hormone levels include intermittent fasting, a healthy diet, eating nutrient-rich foods, nutritional supplements, quality sleep, exercise, and reducing your stress.
FAQs
1. What are the signs of hormonal imbalance?
The most common signs of hormonal imbalance are acne, hot flashes, heavy periods, mood swings, poor sleep, unexplained obesity, low libido, infertility, constipation, and diarrhea.
2. How do you fix your hormonal imbalance?
The best way to fix your hormone health is to identify the primary cause of the imbalance and take natural steps to correct it. General ways to improve hormone production include keto, intermittent fasting, quality sleep, exercise, lowering stress, consuming quality nutrient-dense foods, and taking nutritional supplements.
3. What triggers hormonal imbalance?
Many things can cause different hormonal imbalances, but they all fall under lifestyle changes like; things you eat, things you do, and natural body changes. Monitor them and enjoy hormone balance.
4. What are the symptoms of hormonal imbalance in females?
Dominant symptoms of hormone-related conditions in females include hot flashes, weight gain, fatigue, low libido, menstrual cycle issues, hair loss, and acne.
5. At what age does hormonal imbalance start?
Hormonal imbalance occurs for many women during menopause when the ovaries produce less estrogen and progesterone. This natural transition can start around age 40 or 50.
6. How can I check my hormone levels at home?
There are many different at-home hormone test kits available on the market, including urine, blood, and saliva tests.
7. How long does it take to balance hormones?
Hormone imbalance doesn’t have a fixed duration because many factors can contribute to the imbalance. It’s important to pinpoint the true cause of the imbalance before considering the treatment duration.
8. Can I get pregnant with a hormonal imbalance?
Varying hormone levels can cause certain difficulties with pregnancy, especially related to poor stimulation of estrogen hormones. If you have difficulty getting pregnant, consider having your hormones checked.
9. How can I increase my testosterone naturally?
You can increase your testosterone level naturally by consuming foods rich in zinc, exercising, going on a low-carb diet, and reducing stress.
Previous blog
The Hidden Reason Why You Feel OLDER Than Your AgeNext blog
How Long Does the Keto Flu Last?Tags

Popular
08/31/2023
11.3K views
08/31/2023
14.5K views
08/31/2023
144.5K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




